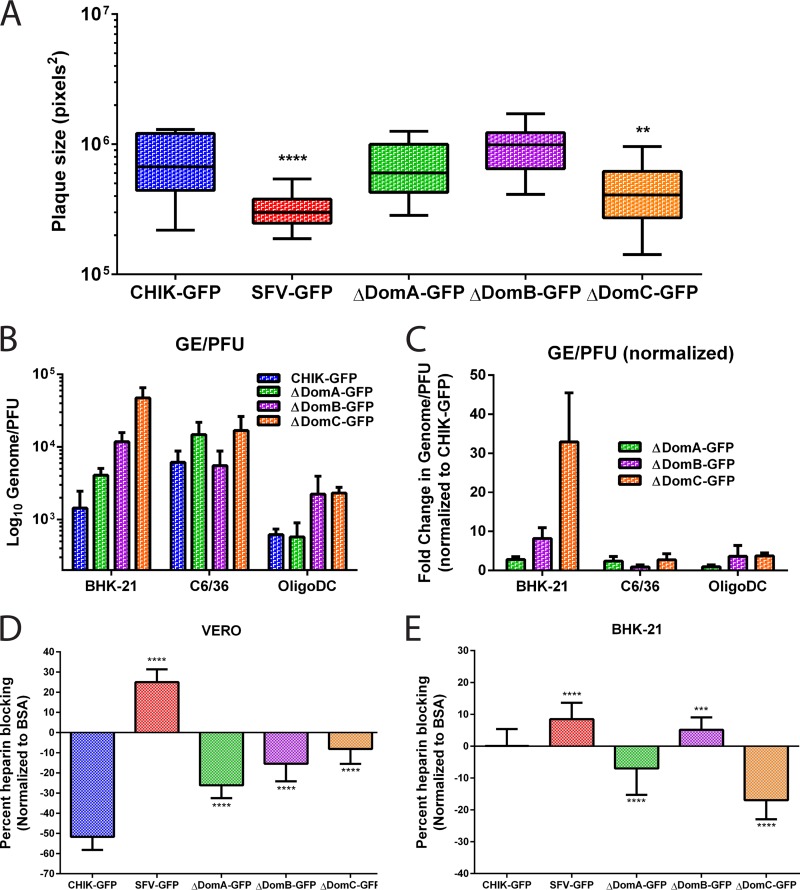
FIG 4.
Plaque size, specific infectivity, and effects of soluble heparin on infectivity of chimeric viruses. (A) Plaque formation after electroporation of parental and chimeric CHIKV/SFV. Infectious clones were electroporated into BHK-21 cells and then mixed with uninfected cells. After attachment, the cells were overlaid with 1.5% CMC media and incubated for 48 h. After incubation, the CMC was discarded, and the cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS and subsequently stained with crystal violet to visualize plaques. Twenty-one plaques for each virus were imaged using an Evos FL microscope, and plaque sizes were measured using ImageJ software. (B and C) Specific infectivity (GE/PFU) of CHIK-GFP and chimeric viruses (B) or GE/PFU values for the chimeric viruses normalized to CHIK-GFP (C). GE/PFU ratios were evaluated in three cell types; BHK-21, C6/36, and OligoDC. (D and E) Effect of soluble heparin on infection of parental or chimeric viruses in Vero (D) or BHK-21 (E) cells. Virus was mixed with heparin or BSA (200 μg/ml) at 4C for 30 min and then used to infect cells. Virus infection was measured using GFP expression as a proxy for virus replication and normalized to both the amount of cells (using Hoechst) and to virus infection with BSA instead of heparin.