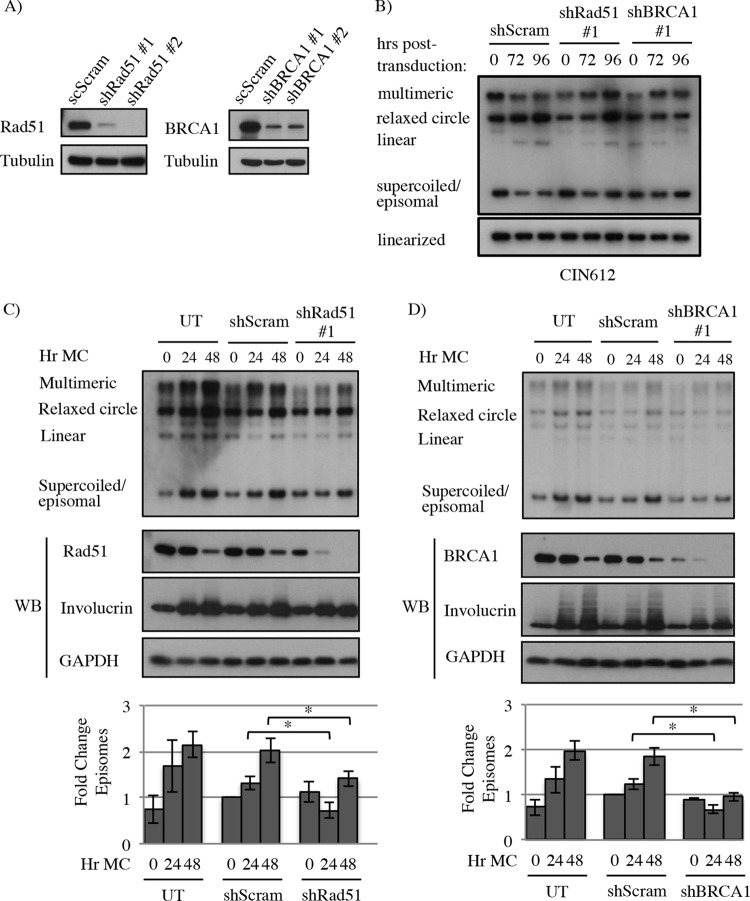
FIG 4.
Knockdown of Rad51 and BRCA1 decreases HPV31 genome amplification upon differentiation. (A) HPV31-positive CIN612 cells were transduced with lentivirus containing control scramble shRNA sequences (scScram) or two shRNA sequences for Rad51 (shRad51) or BRCA1 (shBRCA1) to analyze efficiency of knockdown. Western blot analysis was performed using antibodies to Rad51 and BRCA1. GAPDH served as a loading control. (B) CIN612 cells were transduced with shScram, shRad51 #1, or shBRCA1 #1 and grown as a monolayer for 96 h. DNA was harvested at the indicated times, digested with BamHI (noncutter) or HindIII (which linearizes the viral genome), and examined by Southern blotting for changes in viral episome levels using the HPV31 genome as a probe. (C and D) CIN612 cells were left untreated (UT) or transiently transduced with lentivirus particles containing a control shRNA (shScram), Rad51 shRNA #1, or BRCA1 shRNA #1 for 48 h. At this time, either DNA and protein were harvested as a T0 (undifferentiated) sample or cells were suspended in methylcellulose to induce differentiation for 24 and 48 h. DNA harvested at each time point was analyzed by Southern blotting using the HPV31 genome as a probe. Whole-cell lysates harvested at the indicated time points were analyzed by immunoblotting to demonstrate cellular differentiation (involucrin) and reduced Rad51 or BRCA1 protein in shRNA-transduced cells. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Fold change in episome copy number was determined by performing densitometry of episomal bands from four independent experiments using ImageJ software. Shown is the fold change relative to T0 shScram, which is set to 1. Error bars represent means ± standard errors. *, P ≤ 0.05. WB, Western blot.