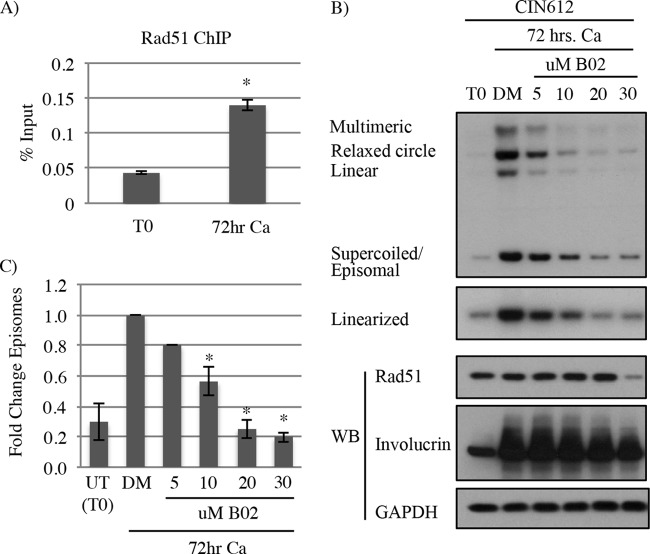
FIG 6.
Inhibition of Rad51 DNA binding activity leads to a defect in productive replication. (A) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) for Rad51 on the HPV31 upstream regulatory region (URR) was performed in CIN612 cells at time zero (undifferentiated) or after 72 h of differentiation in high-calcium medium (Ca). Data for ChIP signals (y axis) from three independent experiments were normalized to 1% of input used. Error bars represent means ± standard errors. *, P < 0.001. (B) DNA and protein were harvested from CIN612 cells at T0 (undifferentiated), as well as after differentiation in high-calcium medium for 72 h in the presence of DMSO (DM) or increasing concentrations of the Rad51 inhibitor B02. DMSO was added at a volume equal to that of the 30 μM concentration of B02. DNA was digested with BamHI (noncutter) or HindIII to linearize the viral genome and then analyzed by Southern blotting for effects on viral copy number using the HPV31 genome as a probe. Western blot analysis was performed to examine the effect of B02 treatment on Rad51 levels and differentiation (involucrin). (C) Effects on episomal copy number were determined by performing densitometry of episomal bands from three independent experiments using ImageJ software. Graphed is the average fold change relative to DMSO (DM)–72-h Ca, which is set to 1. Error bars represent means ± standard errors. *, P < 0.01. Statistics were assayed using a two-tailed t test. Ca, calcium; WB, Western blot.