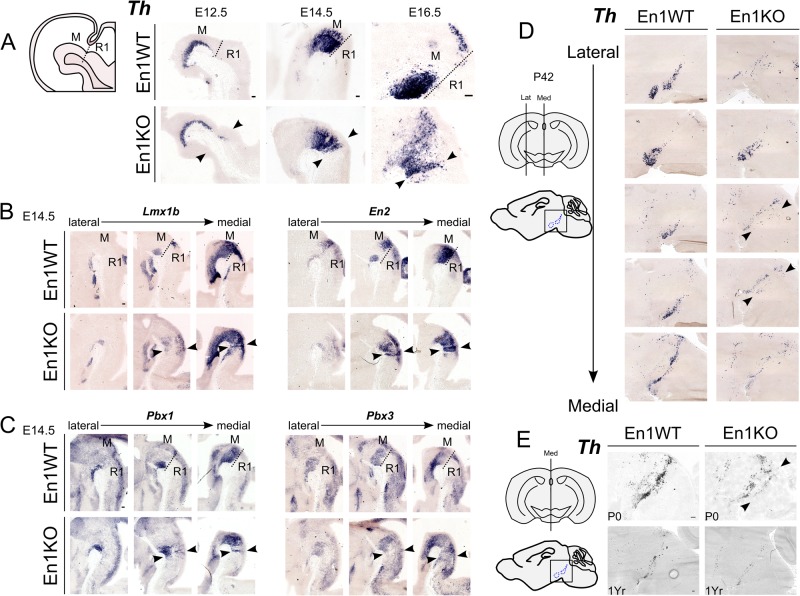
Fig. 1.
Ectopic dopaminergic neurons are found in the hindbrain of the En1KO as early as E12.5 and remain present into adulthood. (A) Th expression is found in the rostral hindbrain of En1 knockout embryos (En1KO) at prenatal stages embryonic day (E)12.5, E14.5 and E16.5 (arrowheads), as compared to wild-type embryos (En1WT). (B,C) Earlier dopaminergic markers, Lmx1b and En2 (B), and transcription factors that are involved in DA subset specification like Pbx1 and Pbx3 (C) are ectopically present in absence of En1 at E14.5 (arrowheads). (D,E) Sagittal sections of neonate and adult En1KO midbrain and hindbrain at postnatal day (P)0 and P42, reveal Th transcript is present in hindbrain (arrowheads). Both the size of the midbrain and ectopic Th-population seems to progressively diminish, as a consequence of the En1-ablation (Veenvliet et al., 2013). At 1 year it is difficult to differentiate between mdDA and eDA neurons. (Para)medial sections as shown in schematic: M, midbrain; R1, rhombomere 1; dotted line represents the position of the isthmus. Scale bars: 100 μm.