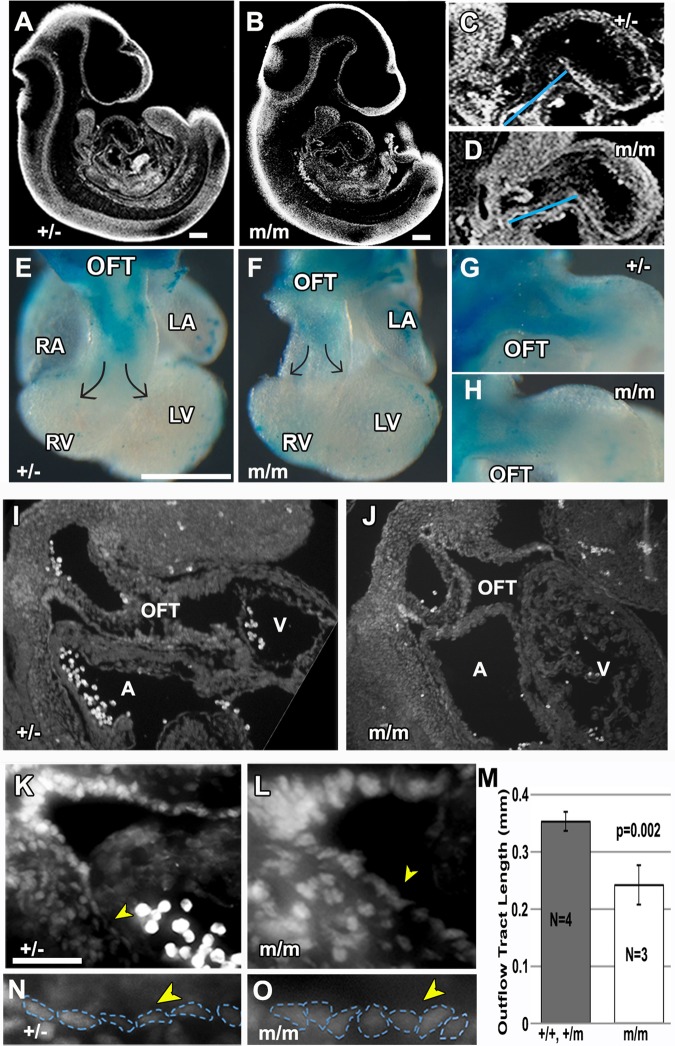
Fig. 2.
Bj mutants have shortened outflow tract and defects in neural crest and second heart field derivatives. (A-D) Episcopic confocal histopathology in the sagittal plane of an E10.5 heterozygous (A) and Bj mutant (B) embryo is shown, with enlarged view of the outflow tract in (C) (n=4) and (D) (n=3) indicating reduction in length of the mutant OFT versus heterozygous (+/−) littermate control (see blue line in C,D). This was confirmed with further quantitative measurements (M). (E-H) Neural crest cells in the outflow tract of E10.5 embryos are visualized via a Cx43-lacZ transgene. This showed a reduction in neural crest cells in the homozygous Bj mutant heart (F,H) as compared to the heterozygous littermate control (E,G). (I-O) Sagittal sections of E10.5 embryo immunostained with anti-Islet1 (Isl1) antibody delineating second heart field cells in the dorsal pericardial wall (DPW) of the outflow tract of a wild-type (I,K) and Bj mutant embryo (J,L), with enlarged views shown in (K) and (L). Cells in the DPW wall (yellow arrowheads, denoted by blue outline in N,O) exhibit a flat squamous epithelial morphology in the wild-type embryo (N), but a distinct cuboidal morphology was observed in the homozygous Bj mutant embryo (O). A, atrium; V, ventricle. (M) Quantitative measurement using histopathology images showed a significant decrease in the length of the OFT in the homozygous Bj mutant hearts as compared to combined wild-type and heterozygous hearts. P-values were calculated with Student's t-test; error bars show standard deviation. Scale bars: 0.5 mm in A-D; 200 µm in E-H.