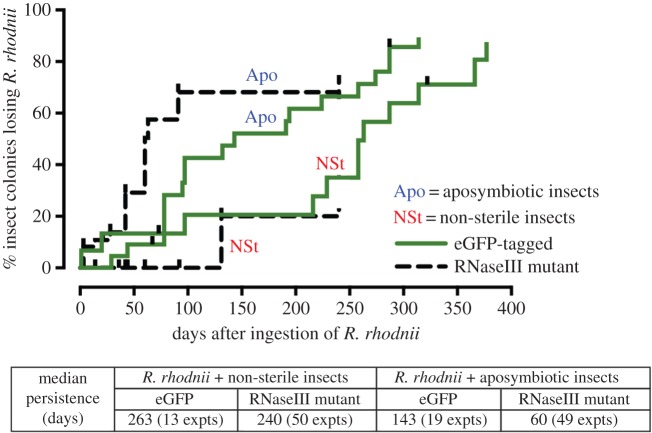
Figure 1.
Persistence of eGFP-expressing and RNaseIII mutant R. rhodnii in R. prolixus, after a single infective feed. The survival chart compares the persistence rate of R. rhodnii following a single per os exposure in non-sterile and aposymbiotic insects. Presence of the bacteria was defined as more than 25 CFUs in samples of excreta, as a proxy for digestive tract colonization. The vertical axis indicates the cumulative percentage of insects losing introduced R. rhodnii (assessed over a period of 240 days for RNaseIII mutant ME315 strain R. rhodnii and 377 days for eGFP-tagged R. rhodnii, commencing 24 h after infective feeding). Vertical ticks indicate censored data (i.e. mortality events in R. rhodnii infected insects). Median bacterial persistence times are indicated in the matrix (with the number of repeat experiments indicated in parentheses). While persistence was compromised in bacteria fed to aposymbiotic insects (p < 0.05 compared with non-sterile insects), there was no significant difference between non-sterile insects fed eGFP-tagged bacteria versus RNaseIII mutant bacteria (Mantel–Cox log-rank test).