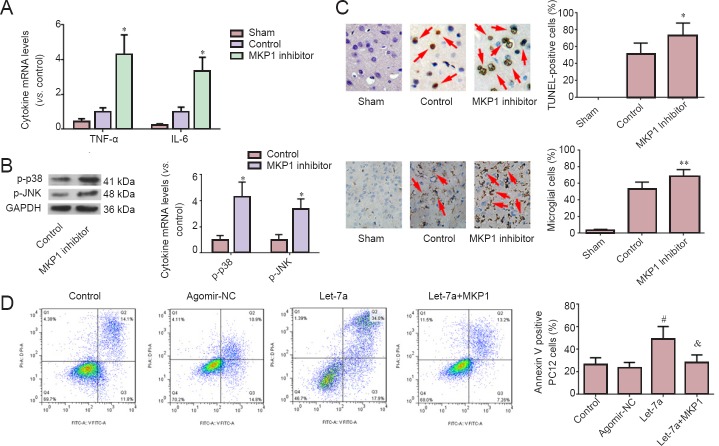
Figure 4.
MKP1 has a neuroprotective effect and lessens the pro-apoptotic effect of let-7a.
(A, B) Inhibition of MKP1 reduced TNF-α and IL-6 release after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury (qRT-PCR, western blot assay), and promoted the activation of p38 MAPK and JNK signaling. (C) Inhibition of MKP1 increased nerve cell (arrows) apoptosis (top panel, TUNEL staining, × 200) and microglial (arrows) activation (bottom panel) after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (immunohistochemical staining, × 400). *P < 0.01, **P < 0.05, vs. control group. (D) MKP1 over-expression relieved a pro-apoptotic effect of let-7a under CoCl2-induced hypoxia. #P < 0.01, vs. agomir-NC; &P < 0.01, vs. let-7a group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 6; A, C, D: one-way analysis of variance and the least significant difference test; B: Student's t-test. TUNEL: Transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-biotin nick end labeling; qRT-PCR: quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; MKP1: mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1; IL-6: interleukin-6; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase; NC: negative control.