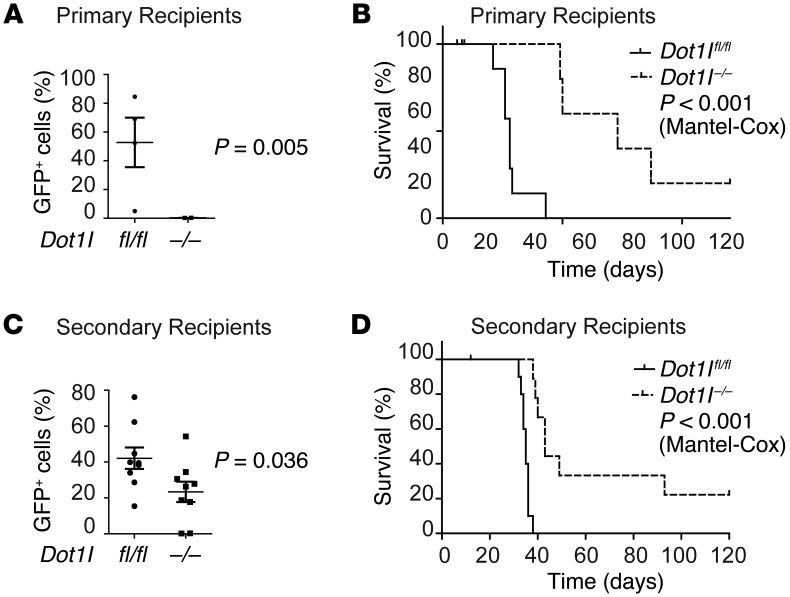
Figure 3. CMP-derived murine MN1-driven leukemia initiation and maintenance are dependent on functional DOT1L in vivo.
(A) Leukemic burden (% of GFP+ cells in the peripheral blood) in recipients on day 20 after injection of MN1 in vitro transformed CMPs (MN1CMP-T) transduced with Cre (Dot1l–/–) or control (Dot1lfl/fl) vector (leukemia initiation). n = 5 (Dot1l–/–) to 6 (Dot1lfl/fl) mice from 2 individual experiments. Two-sided t test Dot1l–/– vs. Dot1lfl/fl. Error bars represent ±SEM. (B) Survival of recipients of MN1 in vitro transformed CMPs (MN1CMP-T) transduced with Cre (Dot1l–/–) or control (Dot1lfl/fl) vector (leukemia initiation). n = 6 (Dot1l–/–) to 7 (Dot1lfl/fl) mice from 2 individual experiments (Mantel-Cox). (C) Leukemic burden (% of GFP+ cells in the peripheral blood) in recipients on day 20 after injection of MN1-driven CMP-derived leukemias (MN1CMP-L) transduced with Cre (Dot1l–/–) or control (Dot1lfl/fl) vector (leukemia maintenance). n = 9 mice per group from 2 individual experiments. Two-sided t test Dot1l–/– vs. Dot1lfl/fl. Error bars represent ±SEM. (D) Survival of recipients of MN1-driven CMP-derived leukemias (MN1CMP-L) transduced with Cre (Dot1l–/–) or control (Dot1lfl/fl) vector (leukemia maintenance). n = 9 (Dot1l–/–) to 11 (Dot1lfl/fl) mice from 2 individual experiments (Mantel-Cox).