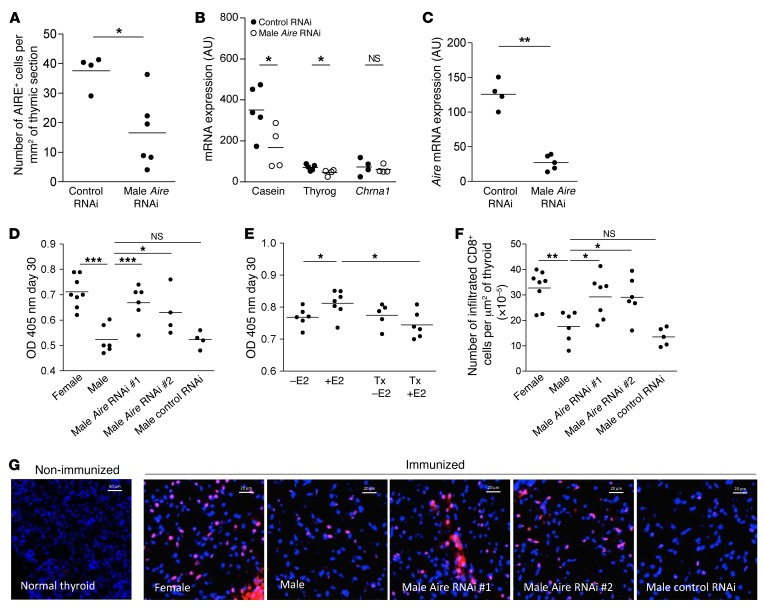
Figure 6. Modulation of AIRE thymic expression by AIRE-miRNAi and its effect on male susceptibility to EAT.
Aire (A) and AIRE-dependent TSA (B) mRNA expression in SJL mouse thymuses at day 6 after scAAV9-miRNAi (850) injection (n = 4–5). Percentage of cells expressing the AIRE protein in the thymic section area (C) of SJL mouse after AIRE scAAV9-miRNAi intrathymic injection (n = 4–6). SJL mice were immunized with 100 nmol of p2340 in CFA emulsion by subcutaneous injections 7 days after intrathymic injection of 2 different AIRE scAAV9-miRNAi. Sera were collected at day 30 and the levels of antibodies to the thyroglobulin peptide p2340 in male, female, and AIRE scAAV9-miRNAi treated-male SJL mice were assessed by ELISA (D) (n = 4–8 sera per group). Bilaterally castrated SJL male mice were thymectomized (TX) and received a subcutaneous injection of 1 μg of estradiol (E2) every 2 days, and were challenged for EAT. Sera were collected at day 30, and the levels of antibodies to the thyroglobulin peptide p2340 were assessed by ELISA (E) (n = 5–7 sera per group). Number of infiltrating CD8-positive cells per μm2 of thyroid (F) (n = 4–8 mice per group). Representative photographs of mouse thyroid immunostaining labeled with an anti-CD8 antibody (red) of nonimmunized and immunized mice (G) for EAT challenge. Images were acquired with a Zeiss Axio Observer Z1 inverted microscope (F). P values were obtained using the Mann-Whitney U test (A–C) and the 1-way ANOVA test (D–F). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.