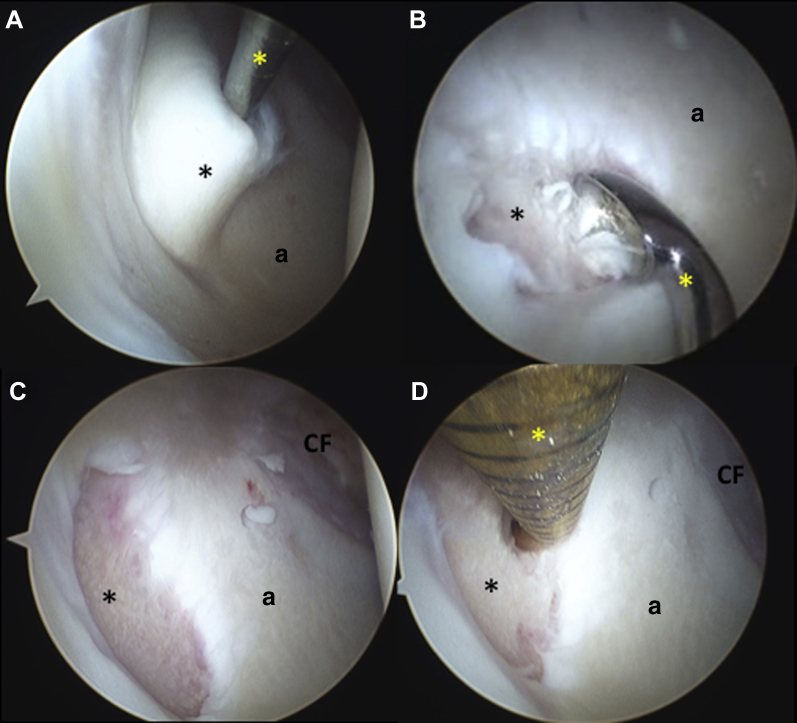
Fig 2.
Intraoperative arthroscopic images corresponding to the right hip in Figure 1. (A) Viewing through the mid-trochanteric portal with a 30° arthroscope, the full-thickness articular cartilage flap (black asterisk) is gently elevated with a probe (yellow asterisk) inserted through the mid-anterior portal. The articular cartilage flap covers the underlying acetabular bone cyst. (B) Viewing through the mid-anterior portal with a 30° arthroscope, an angled curette (yellow asterisk) is inserted through the mid-trochanteric portal to remove the calcified cartilage layer from the articular cartilage defect and to establish a stable rim. The articular communication of the cystic contents (black asterisk) is seen adjacent to the curette. (C) Viewing through the mid-trochanteric portal with a 30° arthroscope, the well-contained articular cartilage defect is seen (black asterisk) after removal of the overlying full-thickness cartilage flap. (D) Viewing through the mid-trochanteric portal with a 30° arthroscope, an angled microfracture awl (yellow asterisk) is inserted through the mid-anterior portal to gently probe and excavate the mucinous contents from the cystic cavity, adjacent to the articular cartilage defect (black asterisk). (a, acetabulum; CF, cotyloid fossa.)