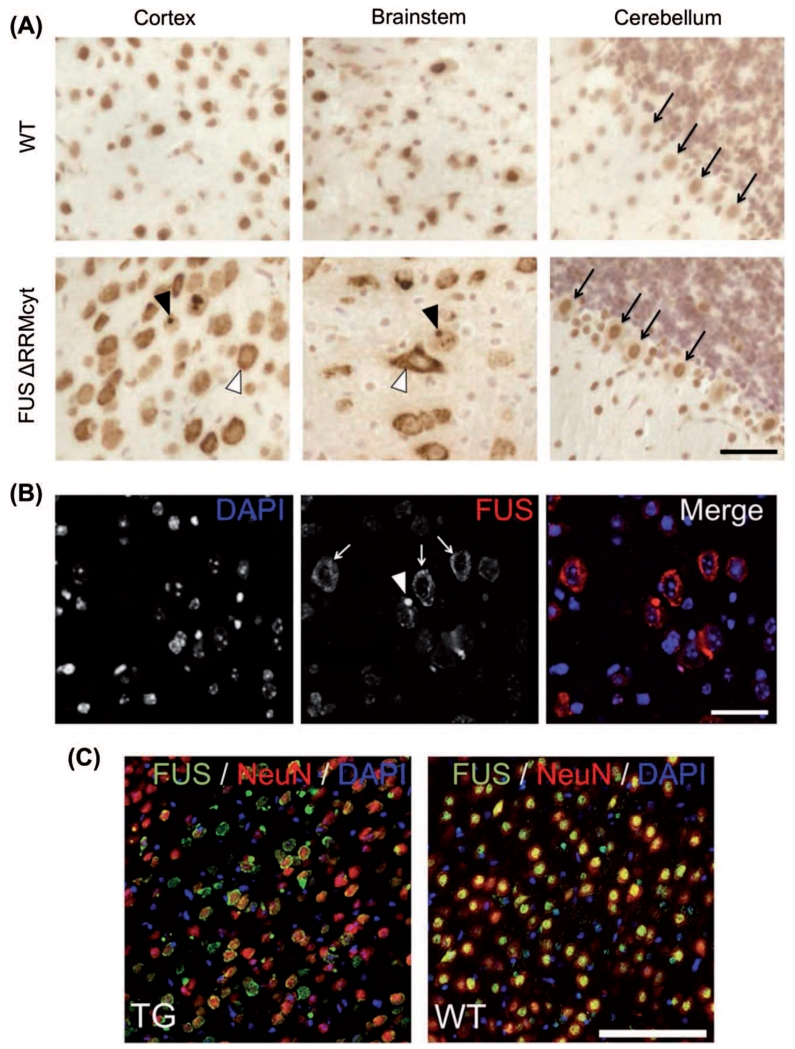
Figure 2. FUS mislocalization in cortical and brainstem neuronal populations in FUS ΔRRMcyt mice.
Mouse brain sections were immunostained with a mouse monoclonal antibody detecting both human mutant and mouse endogenous FUS proteins. (A) Cells of the cortex and brainstem in TG mice displayed prominent FUS immunoreactivity in the cytoplasm (white arrowheads). Large FUS-positive, round inclusions were also frequently observed in the cytoplasm of these cells (black arrowheads). Purkinje cells of the cerebellum (black arrows), however, displayed only very slight staining in the cytoplasm. In WT mice, the cellular localization of FUS is predominantly nuclear. (B) Immunofluorescent staining for FUS and DAPI counterstaining of cell nuclei revealed a granular pattern (white arrows) and the presence of FUS-positive inclusions (white arrowhead) in the cytoplasm of cortical cells. (C) Double immunofluorescent staining for FUS and the neuronal nuclear marker, NeuN, demonstrated that cytoplasmic mislocalization of FUS is widespread in cortical neurons of TG mice. Scale bars: A,B, 25 μm; C, 100 μm.