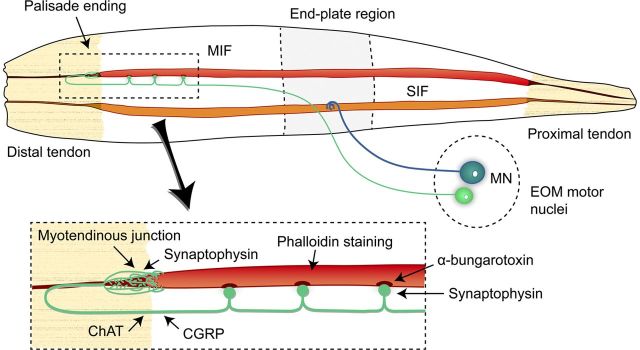
Figure 8.
Schematic drawing summarizing the molecular characteristics, the innervation pattern, and the origin of palisade endings. Palisade endings are located at the proximal and distal myotendinous junctions (only represented in the distal tendon here) and are formed by axons that express choline acetyl transferase and calcitonin gene-related peptide (ChAT/CGRP). Axons forming palisade endings establish α-bungarotoxin-positive contacts along the muscle fibers. Motoneurons (MN) contacting multiply innervated muscle fibers (MIF) in the EOM motor nuclei give rise to palisade endings, as demonstrated by anterograde transport of BDA. SIF indicates singly innervated muscle fiber.