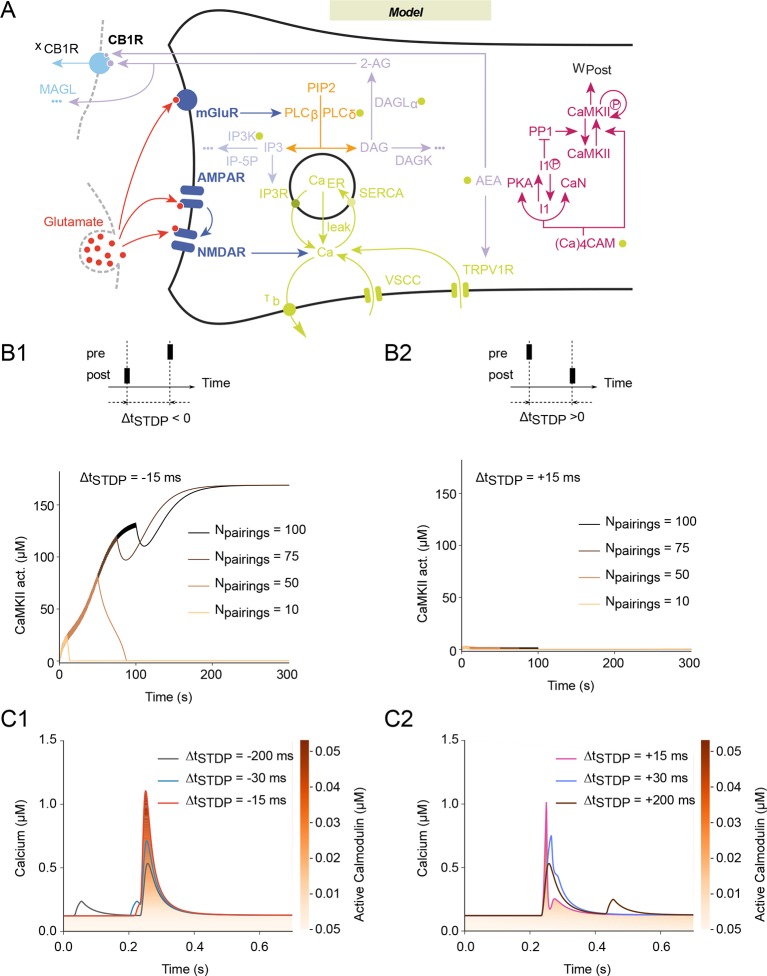
Figure 2. Mathematical model predicts NMDAR-tLTP with large numbers of post-pre pairings.
(A) Scheme of the modeled signaling network. The synaptic weight Wtotal is the product of pre- and postsynaptic weights Wpre and Wpost. The NMDAR-based pathway sets Wpost as the phosphorylation state of postsynaptic CaMKIIα. In the second pathway, coincident activation of phospholipase Cβ by postsynaptic mGluR and calcium entry via VSCC and TRPV1 induces the production of 2-AG and AEA. 2-AG, and to a lower extent AEA, activates CB1R (xCB1R is the fraction of non-desensitized CB1R), which then modulates the presynaptic weight, Wpre. Color code: glutamate receptors: dark blue; PLC pathway: yellow; IP3 pathway: powderblue; calcium pathways: green (green disks indicate calcium-dependent steps); DAGLα pathway: lavander; AEA pathway: light blue; CB1R pathway: blue. Abbreviations: PIP2: phospatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate; DAG: diacylglycerol; IP3: inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate; PLCβ/δ: phospholipase C β/δ; DAGK: diacylglycerol kinase; IP-5P: inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase; IP3K: IP3-kinase; DAGLα: diacylglycerol lipase α;B/BCa: free/bound endogeneous calcium buffer; IP3R: IP3-receptor channel; SERCA: sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase; CaER: calcium in the endoplasmic reticulum; (Ca)4CaM: fully bound calmodulin; CaN: calcineurin aka PP2B; PKA: protein kinase A; I1p/I1: phosphorylated/unphosphorylated protein phosphatase 1 inhibitor 1 (DARPP-32 in striatal output neurons); PP1: protein phosphatase 1; pCaMKII/CaMKII: phosphorylated/unphosphorylated CaMKII; DAGK: diacylglycerol kinase; MAGL: monoacylglycerol lipase; the '…' sign indicates transformation into products that are considered not to interfere with the other interactions of the model. (B) Corresponding changes in the levels of active CaMKII starting from the down (non-activated) state. The number of pairings, Npairings, is indicated for 1 Hz pairings at spike-timing ΔtSTDP=-15 (B1) or +15 (B2) ms. (C) Intracellular calcium changes for the first pairing in post-pre (C1) or pre-post (C2) pairing protocols. The colorcode shows the corresponding amount of calmodulin activation according to the colorbar.