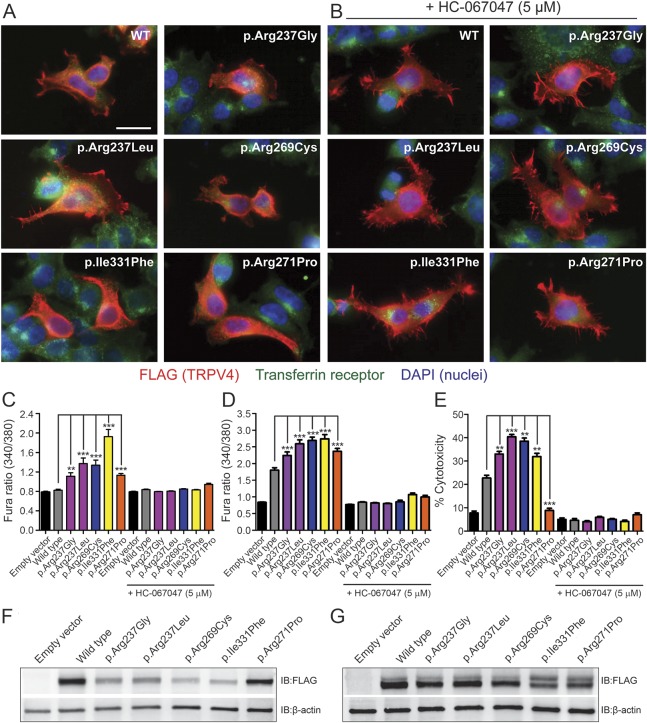
Figure 3. p.Arg237Gly and p.Arg237Leu mutations do not alter the subcellular localization of TRPV4 but cause elevations of basal [Ca2+]i and significant cytotoxicity.
(A, B) Representative images of HEK293T cells transfected with wild-type (WT) or mutant TRPV4-FLAG and labeled immunocytochemically for FLAG (red) to reveal the subcellular distribution of TRPV4. Cells were costained for the transferrin receptor (green) and with DAPI (blue) to delineate individual cells and nuclei, respectively. These studies included examination of known neuropathy–causing (p.Arg269Cys), skeletal dysplasia–causing (p.Ile331Phe), and osteoarthropathy-causing (p.Arg271Pro) TRPV4 mutations. Transfected cells were cultured in the absence (A) or presence (B) of the TRPV4 antagonist HC-067047 (5 μM). All images are shown at the same magnification, and the scale bar represents 20 μm. (C, D) Quantification of baseline Fura-2 ratios in transiently transfected MN-1 (C) and HEK293T (D) cells reveals significant increases in basal [Ca2+]i with expression of each mutant channel that are blocked by the TRPV4 antagonist HC-067047 (5 μM). (E) Quantification of cell death in HEK293T cells 24 hours after transfection using an LDH cytotoxicity assay. Cells expressing TRPV4 mutants, with the exception of p.Arg271Pro, show significantly increased levels of cytotoxicity relative to TRPV4WT-expressing cells; this increase is abrogated by HC-067047 (5 μM). **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001. Data in C and D are averaged from >100 transfected cells, while data in E are averaged from 3 independent transfections. Error bars, SEM. (F, G) Immunoblotting of whole lysates from HEK293T cells 24 hours after transfection incubated in the absence (F) or presence (G) of HC-067047 (5 μM).