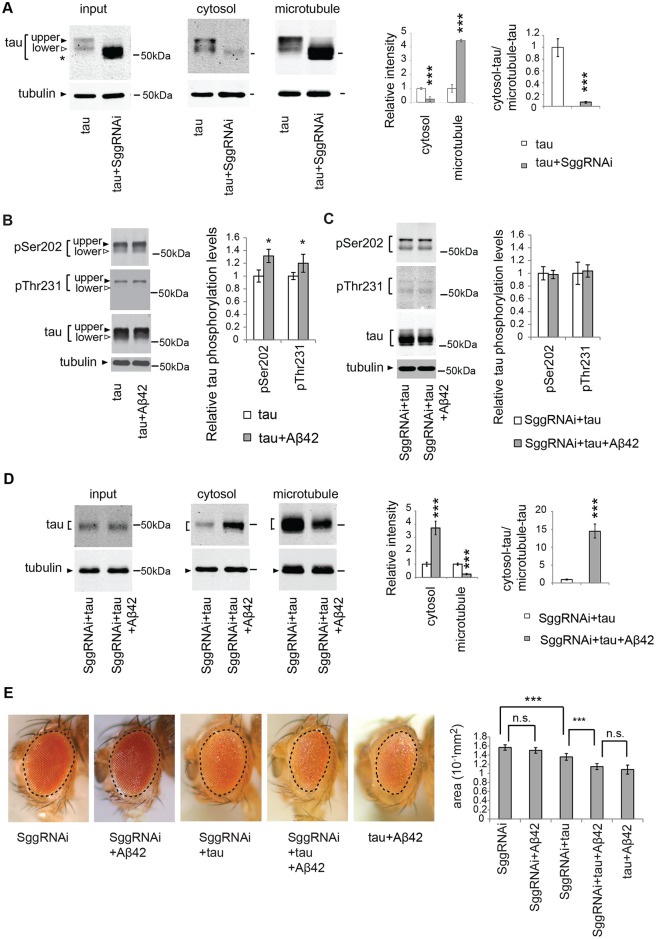
Fig 2. Knockdown of GSK3β/Sgg is not sufficient to suppress either mislocalization of tau to the cytosol or Aβ42-induced augmentation of tau toxicity.
(A) GSK3β/Sgg negatively regulates tau binding to microtubules. RNAi-mediated knockdown of GSK3/Sgg shifts all tau species to lower apparent molecular weights, and the resultant species migrate faster than the original taulower species (indicated as asterisk). The levels of tau and tubulin in the lysate before sedimentation (input), in the supernatant (cytosol) and in the pellet containing microtubules (microtubule) were analyzed by western blotting by using anti-tau antibody. The same amount of proteins from each genotype was loaded. Mean ± SD, n = 4; **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.005 by Student's t-test. Representative blots are shown. (B) Aβ42 increased the levels of tau phosphorylated at Ser202 and those phosphorylated at Thr231. Western blots of fly heads expressing tau alone (tau) or that co-expressing tau and Aβ42 (tau+Aβ42) with anti-phospho-Ser202 antibody (pSer202), anti-phospho-Thr231 antibody (pThr231), and anti-tau antibody. Tubulin was used as a loading control. Mean ± SD, n = 5; *, p < 0.05 by Student's t-test. Representative blots are shown. (C) Expression of Aβ42 did not increase tau phosphorylation at either of Ser202 and Thr231 in the Sgg knockdown background. Western blots of fly heads expressing Sgg RNAi tau and (SggRNAi+tau) or that co-expressing Sgg RNAi, tau and Aβ42 (SggRNAi+tau+Aβ42) with anti-phospho-Ser202 antibody (pSer202), anti-phospho-Thr231 antibody (pThr231), and anti-tau antibody. Tubulin was used as a loading control. Mean ± SD, n = 5; no significant difference by Student's t-test (p > 0.05). Representative blots are shown. (D) Aβ42 causes an increase in tau levels in the cytosol fraction and reduction in tau levels in the microtubule fraction in the Sgg knockdown background. The levels of tau and tubulin in fly heads expressing Sgg RNAi and tau (SggRNAi+tau) or that co-expressing Sgg RNAi, tau and Aβ42 (SggRNAi+tau+Aβ42) before sedimentation (input), in the supernatant (cytosol) and in the pellet containing microtubules (microtubule) were analyzed by western blotting with anti-tau and anti-tubulin. Mean ± SD, n = 4; ***, p < 0.005 by Student's t-test. Representative blots are shown. (E) Aβ42 enhances tau-induced retinal degeneration in the Sgg knockdown background (compare SggRNAi+tau and SggRNAi+tau+Aβ42). Mean ± SE, N = 6–8, asterisks indicate significant differences in the surface area of the external eye (***, p < 0.005, n.s., not significant (p > 0.05) by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test). Transgene expression was driven by gmr-GAL4.