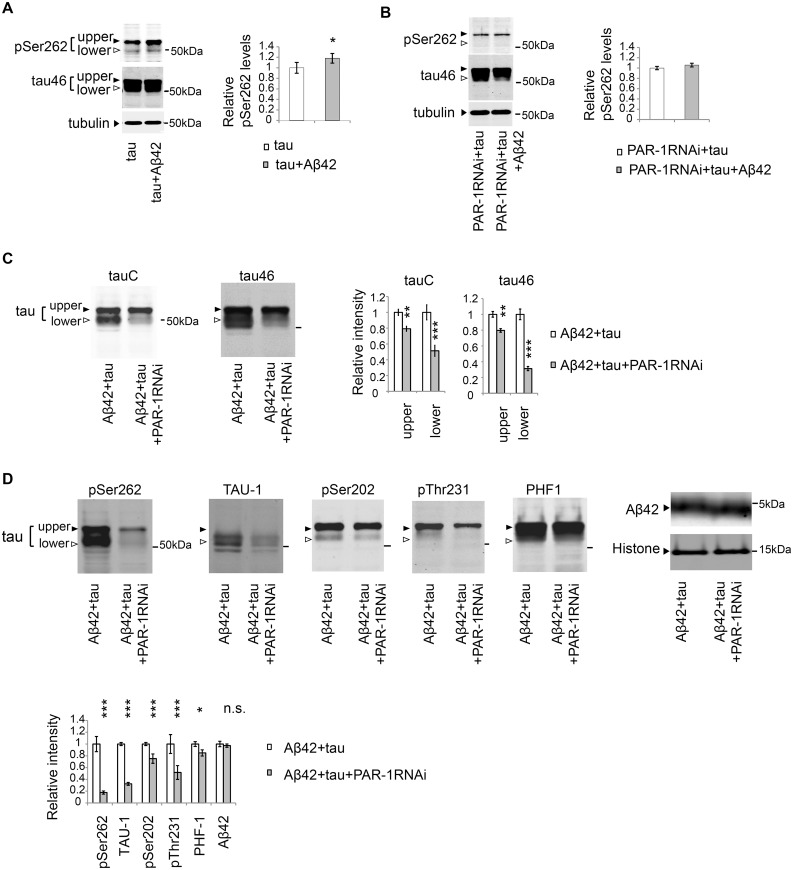
Fig 5. PAR-1 mediates the increase in the level of tau phosphorylated at Ser262 caused by Aβ42, and knockdown of Par-1/MARK markedly decreases the levels of taulower.
(A) Aβ42 increased the levels of tau phosphorylated at Ser262. Western blots of fly heads expressing tau alone (tau) or that co-expressing tau and Aβ42 (tau+Aβ42) with anti-phospho-Ser262 antibody (pSer262) or anti-tau (tau46). Tubulin was used as a loading control. Mean ± SD, n = 5; *, p < 0.05 by Student's t-test. Representative blots are shown. (B) Expression of Aβ42 did not increase tau phosphorylation at Ser262 in the PAR-1 knockdown background. Western blots of fly heads expressing PAR-1 RNAi and tau (PAR-1RNAi+tau) or that co-expressing PAR-1RNAi, tau and Aβ42 (PAR-1RNAi+tau+Aβ42) with anti-phospho-Ser262 antibody (pSer262) and anti-tau antibody (tau46). Tubulin was used as a loading control. Mean ± SD, n = 5; no significant difference by Student's t-test (p > 0.05). Representative blots are shown. (C-D) PAR-1 knockdown reduces the levels of tau with more prominent effect on the levels of taulower than those of tauupper. Western blots of fly heads expressing Aβ42 and tau (Aβ42+tau) or that co-expressing Aβ42, tau and PAR-1 RNAi (Aβ42+tau+PAR-1RNAi) with pan-tau antibody (tauC and tau46), antibodies that recognize phosphorylation status of tau at the specific sites (pSer262, TAU-1, pSer202, pThr231, PHF-1) or anti-Aβ antibody (Aβ42). Histone was used as loading control. Mean ± SD, n = 5; *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p<0.005. Representative blots are shown. Transgene expression was driven by gmr-GAL4.