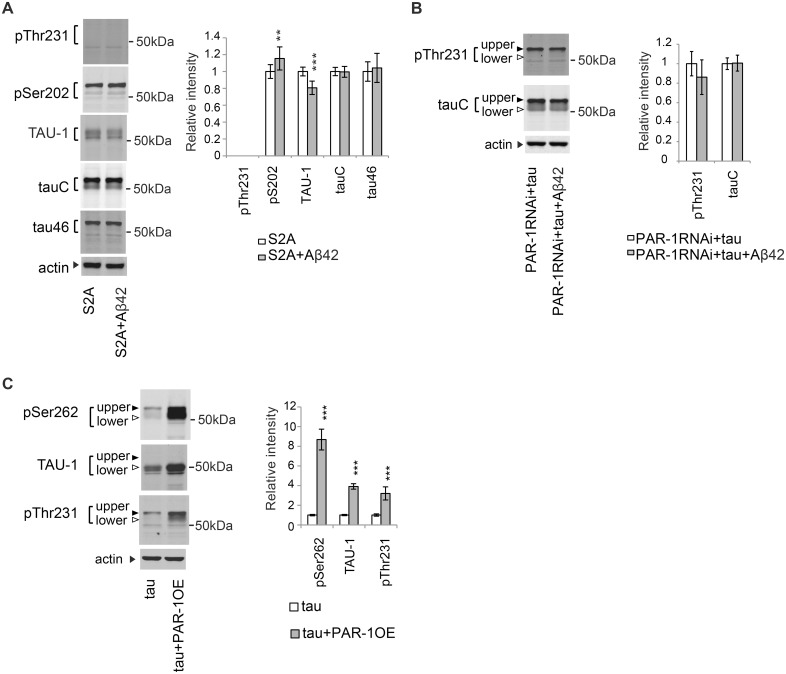
Fig 7. Stabilization of tau through phosphorylation at Ser262 and Ser356 contributes to the Aβ42-induced increase in the level of tau phosphorylated at Thr231.
(A) Aβ42 does not increase the levels of S2Atau phosphorylated at Thr231. Western blots of fly heads expressing S2Atau (S2A) or that co-expressing S2Atau and Aβ42 (S2A+Aβ42) with antibodies that recognize phosphorylation status of tau at the specific sites (pThr231, pSer202, and TAU-1) or pan-tau antibodies (tauC and tau46). (B) Aβ42 does not increase the levels of tau phosphorylated at Thr231 in the PAR-1 knockdown background. Western blots of fly heads expressing PAR-1RNAi and tau (PAR-1RNAi+tau) or that co-expressing PAR-1RNAi, tau and Aβ42 (PAR-1RNAi+tau+Aβ42) with anti-phospho-Thr231 antibody (pThr231) or pan-tau antibody (tauC). (C) PAR-1 overexpression increases the levels of tau phosphorylated at Thr231. Western blots of fly heads expressing tau (tau) or that co-expressing PAR-1 and tau (tau+PAR-1OE) with anti-phospho-Ser262 antibody (pSer262), TAU-1 or anti-phospho-Thr231 antibody (pThr231). Actin was used as loading control. Mean ± SD, n = 5; **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.005. Representative blots are shown. Transgene expression was driven by gmr-GAL4.