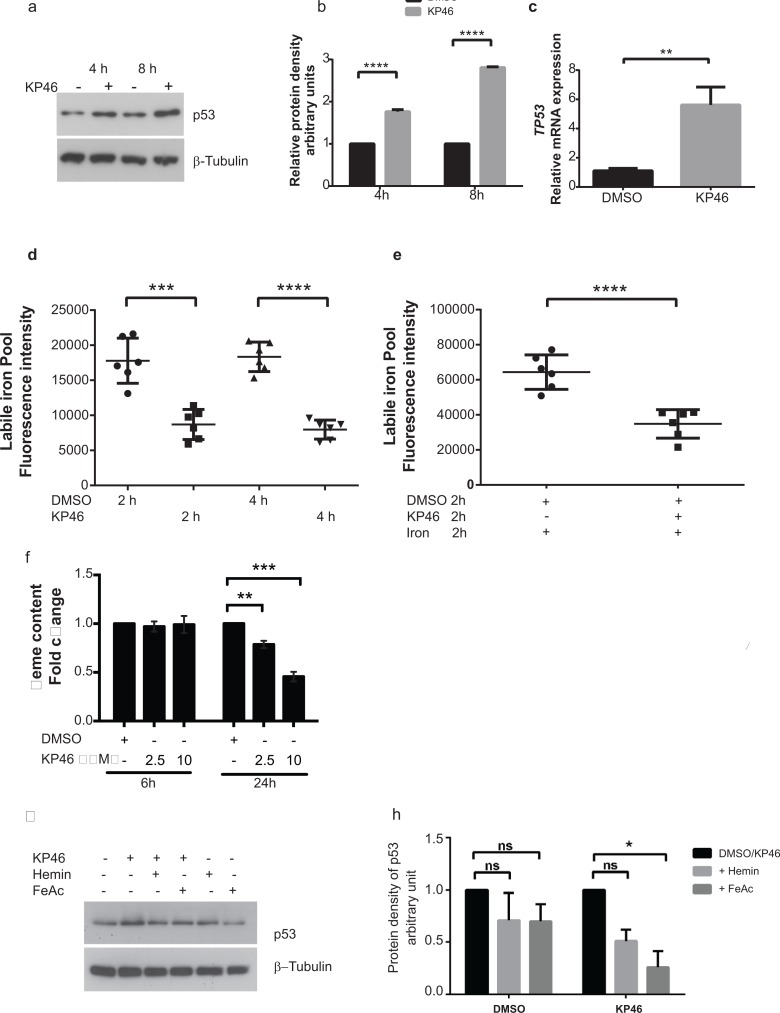
Figure 5. KP46 upregulates p53 in an iron dependent manner.
a–b. Early upregulation of p53. HCT116WT cells were exposed to vehicle or 10 μM KP46 for 4 or 8 hours. a. Protein lysates were immunoblotted against anti p53.β-Tubulin served as loading control. b. Quantification of the protein density of p53 for 4 and 8 hours relatively to β-Tubulin. n = 3, ±SEM, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test, c. KP46-changed TP53 transcript expression. mRNA analyses of HCT116WT cells exposed to vehicle or 10 μM KP46 for 4 hours were performed by RT-PCR. Shown is the mean normalized gene expression of TP53, mean values ±SD (n = 3 independent measurements, carried out as triplicates), **p-value = 0.0029 using Students t-test two tailed unpaired d–e. KP46 decreases the labile iron pool. Labile iron pool (LIP) of cells exposed to vehicle or 10 μM KP46 were measured for 2 and 4 hours (d) or to iron (FeAc, 600 nM) plus vehicle or plus 10 μM KP46 for 2 hours (e) (n = 2 independent LIP measurements performed in triplicates). Shown is the mean total fluorescence intensity of calcein measured at Ex485/Em535 nm ±SD. ***p < 0.001 ****p < 0.0001 versus control using one-way ANOVA, two-tailed, unpaired followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. f. KP46 decreases the intracellular heme content. Cells were treated with vehicle or KP46 for the indicated length of time in growth media. Data shown are mean fold changes of protoporphyrin IX relative to the DMSO controls ±SEM (n = 3 independent experiments). **p < 0.01,***p < 0.001 using one way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison. g–h. KP46 upregulated p53 is reverted by iron and heme. HCT116WT cells were loaded with FeAc (600 μM) or hemin (10 μM) for 6 hours, washed twice with or without DTPA (50 μM), respectively, prior to exposure to vehicle or 10 μM KP46 for 8 hours. g. Protein lysates were immunoblotted as in (a). h. Quantification of the relative iron- and hemin- mediated protein decrease of p53. *p < 0.05, n = 3, ±SEM, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test.