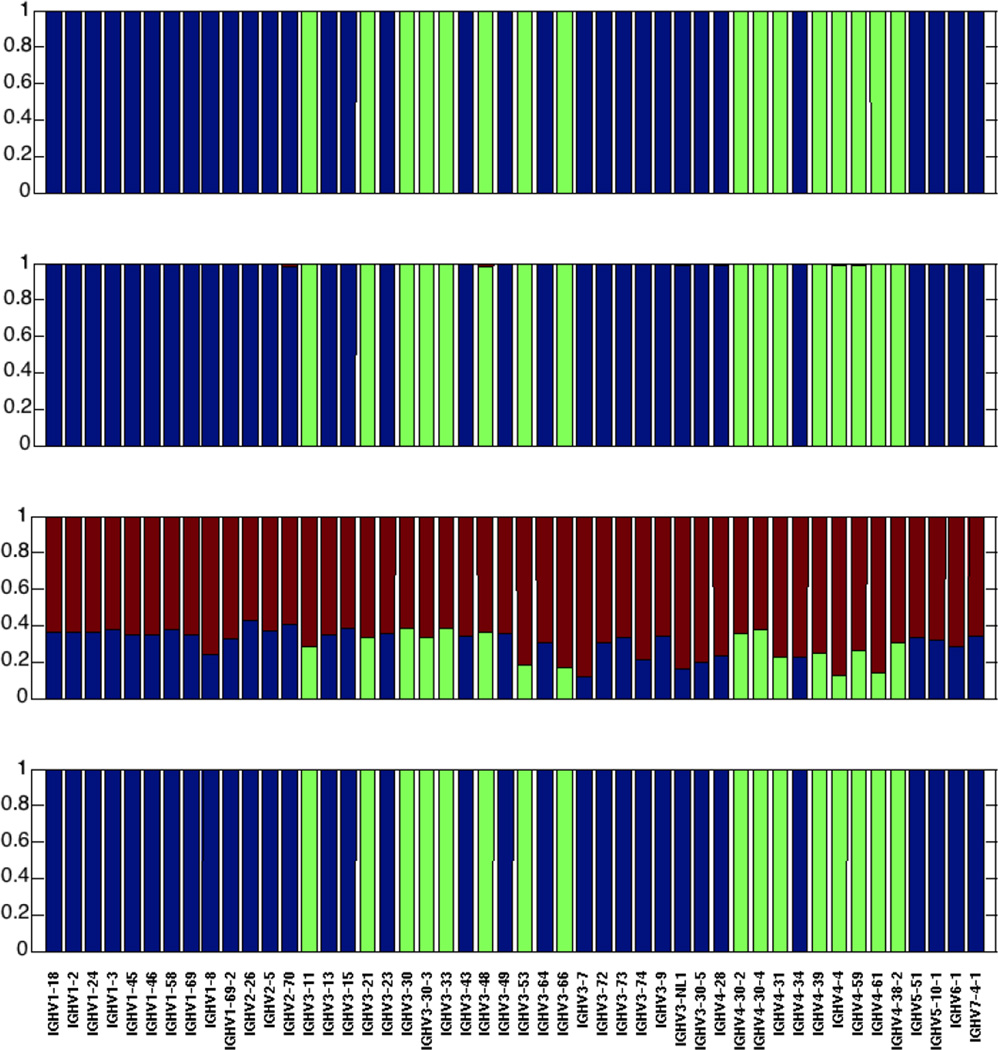
Figure 5. Comparison of human VH identification results using three different sequence identification methods at n=150 nucleotide read length and 0.15 mutation frequency.
From top to bottom (A) The Anchor method (this paper); (B) High V-Quest; (C) IgBLAST using the default word length (9 characters); (D) IgBLAST using the minimal word length (4 characters). In all cases the blue color represents the fraction of correctly identified sequences in which a VH gene is uniquely identifiable; green is the fraction of identifications when a gene is not distinguishable from at least one other gene (using the calculation described in the Calculation and Methods section) and either the real gene or the one we predict to confuse it with are identified; red is the fraction of incorrect identifications.