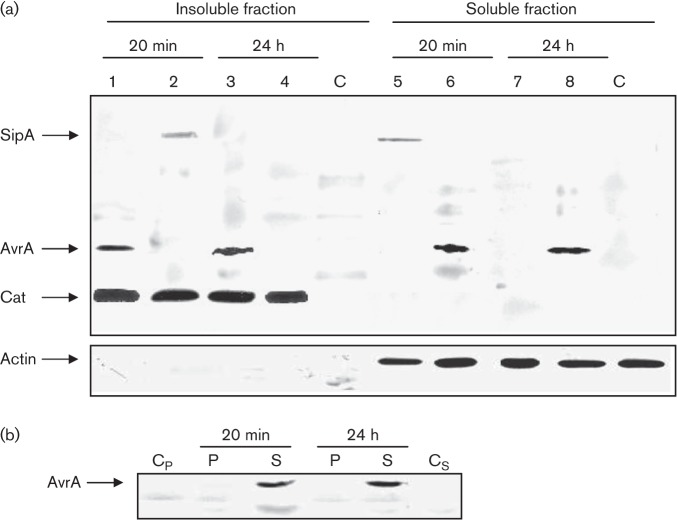
Fig. 2.
Analysis of AvrA expression, translocation (a) and localization (b) in HEp-2 cells by Western blot. Epithelial cells were infected with SipA-tagged and AvrA-tagged strains of S. Enteritidis for 20 min and 24 h. (a) Post-infection cells were processed as indicated in Methods to obtain an insoluble fraction containing intact bacteria and a soluble fraction containing translocated effectors. Both fractions were analysed by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG antibodies. Lanes: 1, 3, 6 and 8, SE1702 (avrA : : 3×FLAG cat : : FLAG); 2, 4, 5 and 7, SE1703 (sipA : : 3×FLAG cat : : FLAG); C, control uninfected cell cultures. As a control for the host-cell cytosolic fraction some blots were reprobed with polyclonal antibodies to actin. (b) Subcellular localization of AvrA. Epithelial cells were infected with an AvrA-tagged strain of S. Enteritidis for 20 min and 24 h, and were fractionated into membrane insoluble (P) or soluble fractions (S) as described in Methods. Both fractions were analysed by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG antibodies. Cp and Cs, negative controls (pellet and soluble fraction from uninfected cell cultures, respectively). Each lane was loaded with material from approximately 106 c.f.u. bacteria. Data are representative from three independent experiments.