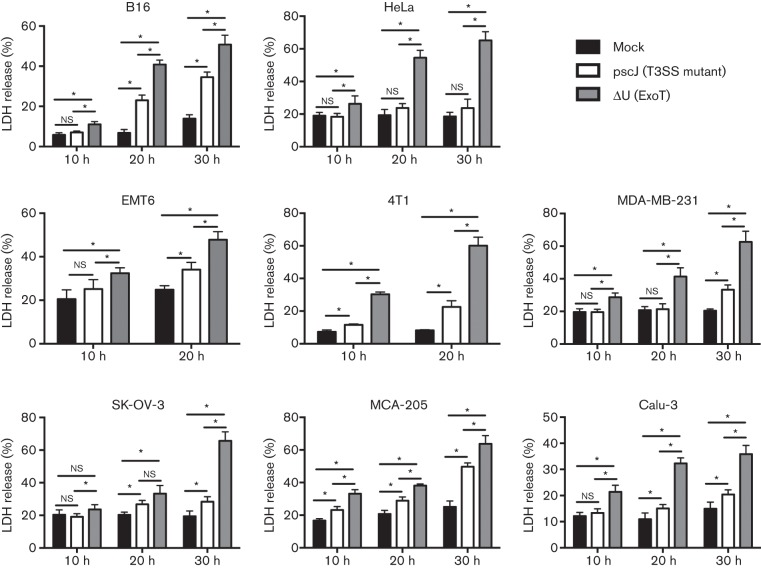
Fig. 1.
Infection with ExoT-expressing P. aeruginosa can cause cytotoxicity in a number of cancer cell lines. The indicated cancer cells were either infected with ExoT-expressing (ΔU) or ExoT-defective T3SS mutant (pscJ) P. aeruginosa isogenic strains at m.o.i.~10, or cultured in media alone. Media were collected at 10 h intervals over a 30 h period and the amount of LDH released into media was analysed using the LDH release assay. The per cent LDH release was determined by the ratio of experimental LDH release to the total LDH release in the presence of Triton X-100. Analysis of LDH release of infected cancer cells, especially at later time points, indicated that infection with ExoT-expressing ΔU resulted in significantly more cytotoxicity compared with cells treated with the pscJ strain or left uninfected. *P<0.05, n = 6, Student’s t-test.