Figure 1. Homozygosity mapping and whole exome sequencing (WES) identify recessive mutations of NUP93, NUP205, or XPO5 in 8 families with steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome.
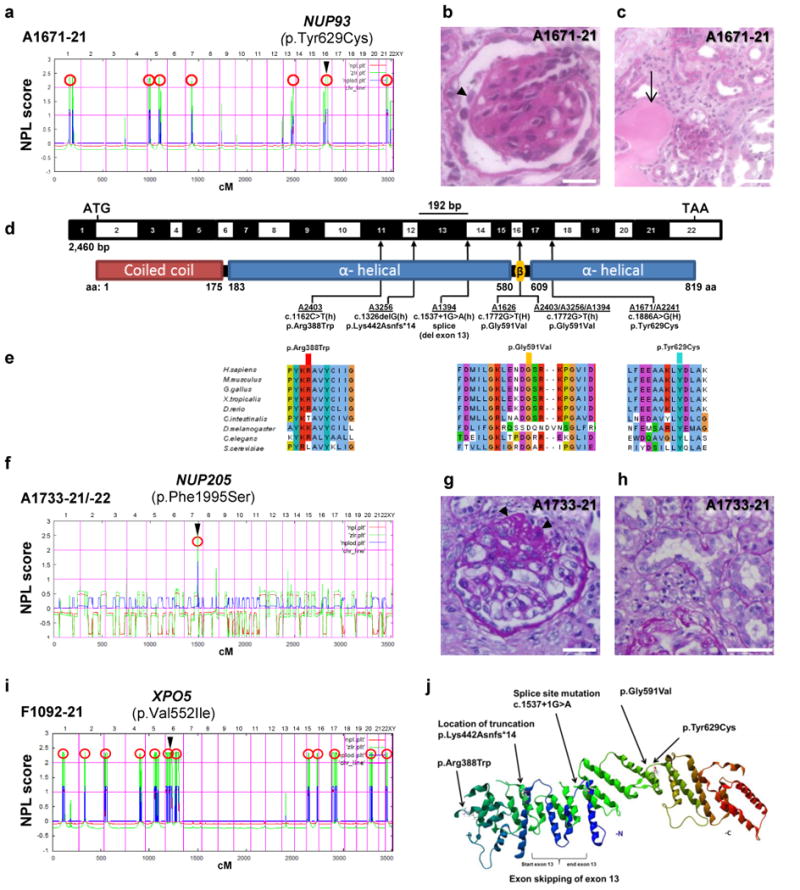
(a) Homozygosity mapping identifies seven recessive candidate loci (red circles) in family A1671 with steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS), and WES identifies a homozygous mutation of NUP93 (p.Tyr629Cys). The NUP93 locus (arrowhead) is positioned within one of the maximum NPL peaks on chromosome 16q. (b–c) Renal histology of A1671-21 shows diffuse mesangial sclerosis (arrowhead) (b) and tubular dilation with protein casts (arrow) as well as tubular interstitial infiltration and fibrosis (c). (d) Exon (black-white) and protein domain (red-blue) structure of human NUP93 cDNA. Black bar denotes in-frame deletion of exon 13 (192 bp) resulting from a c.1537+1G>A mutation in family A1394-21. Three homozygous and three compound-heterozygous NUP93 mutations detected in 6 families with SRNS. Arrows indicate positions of mutations in relation to exons and protein domains. h, heterozygous; H, homozygous. (e) Conservation across evolution of altered amino acid residues for the three NUP93 missense mutations (p.Arg388Trp, p.Gly591Val, p.Tyr629Cys). (f) Genetic linkage mapping and WES in family A1733 with SRNS identifies a homozygous mutation in NUP205 (p.Phe1995Ser). (g–h) Renal histology sections of A1733 showing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). (i) Homozygosity mapping and WES in family F1092 with SRNS identifies a homozygous mutation in XPO5 (p.Val552Ile). (j) 3D structure of Nic96, the S. cerevisiae ortholog of human NUP93 (PDB 2QX5) lacking the coiled-coil domain. Scale bars are: (b,g) 25 μm, (c) 100 μm, and (h) 50 μm.
