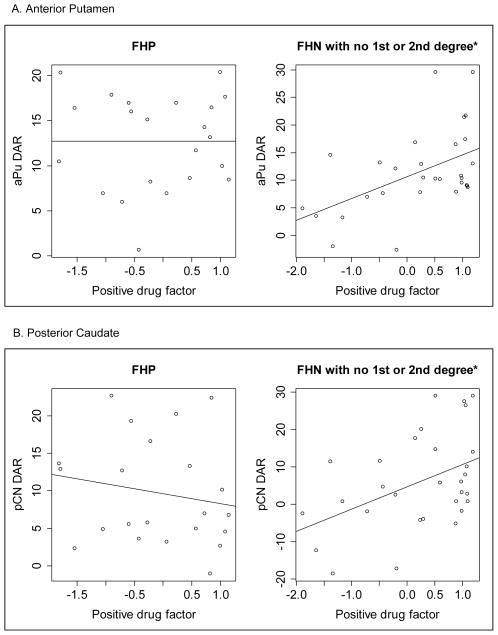
Figure 1.
Correlation of change in dopamine binding potential (ΔBPND) and subjective amphetamine-induced positive drug effects by family history of alcohol use disorder in A) the anterior putamen (aPU), and B) posterior caudate (pCN). Family history positive (FHP) subjects had at least one 1st degree family member with AUD and family history negative (FHN) subjects had no 1st or 2nd degree family members with AUD. * p ≤ 0.05.