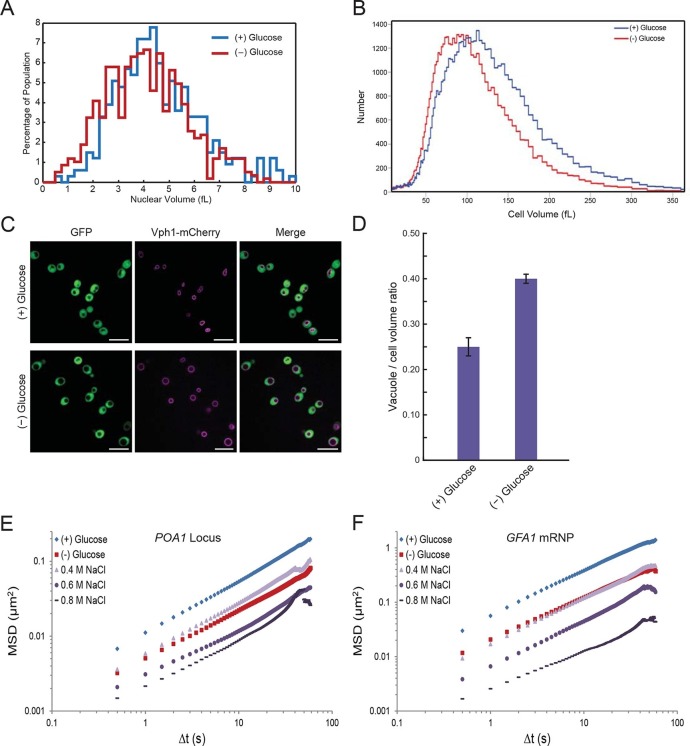
Figure 5. Starvation induces a constriction in cell size and an expansion in vacuolar volume (Figure 5—figure supplements 1 and 2).
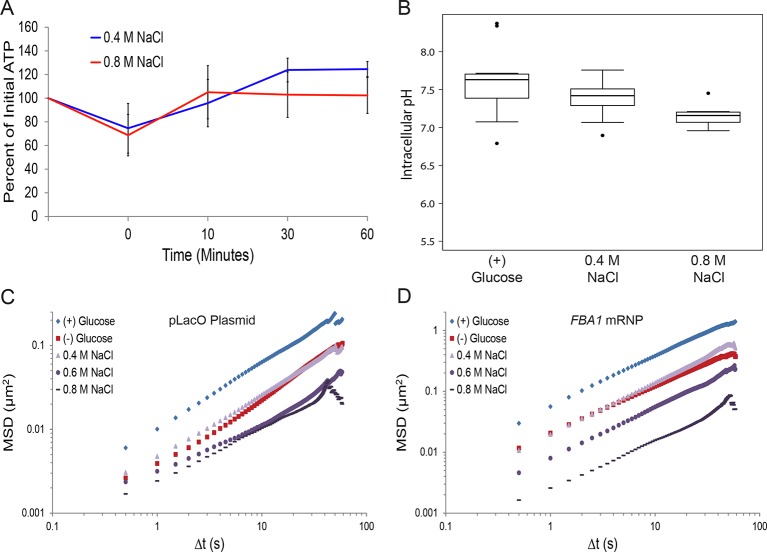
(A) Nuclear volume after acute glucose starvation. Histograms of nuclear volumes measured by reconstruction from three-dimensional image stacks using Imaris. The p-value resulting from a two-tailed t-test on the average volume in each condition (unpaired values assuming equal variance) is p<0.001. (B) Histograms of cell volumes of log-growing and acutely starved yeast cells. Log-growing cells, (+) glucose, were acutely starved of glucose, (–) glucose, and cell volume was measured using a Beckman Coulter Multisizer 3 (see 'Materials and methods'). Approximately 50,000 cells were measured for each condition. (C) Cytoplasmic free GFP (green) and vacuolar membrane protein Vph1-mCherry (magenta) fluorescence images. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) Quantification of vacuole-to-cell volume ratio. Error bars represent standard errors about the mean (N = 3 independent experiments with > 55 cells per experiment). (E) Log-log MSD plot of the POA1 locus after treatment with increasing concentrations of NaCl. Cells were imaged approximately 10 min after hyperosmotic shock. (F) Log-log MSD plot of the GFA1 mRNP after treatment as described in (E).
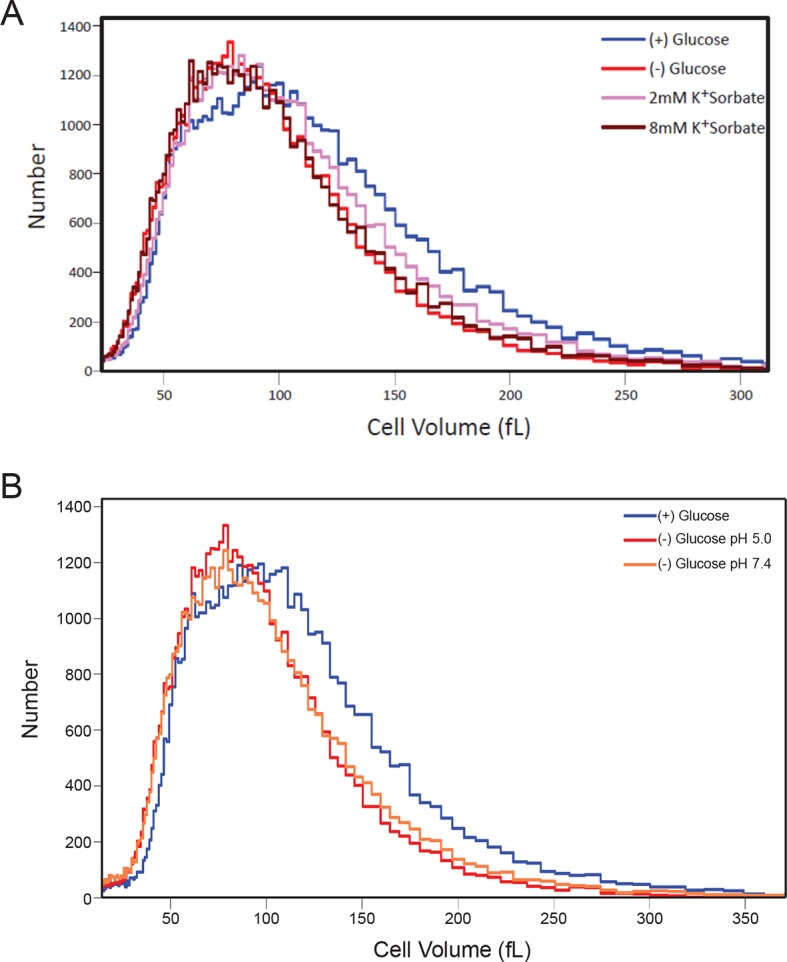
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Histograms of cell volumes after various treatments.