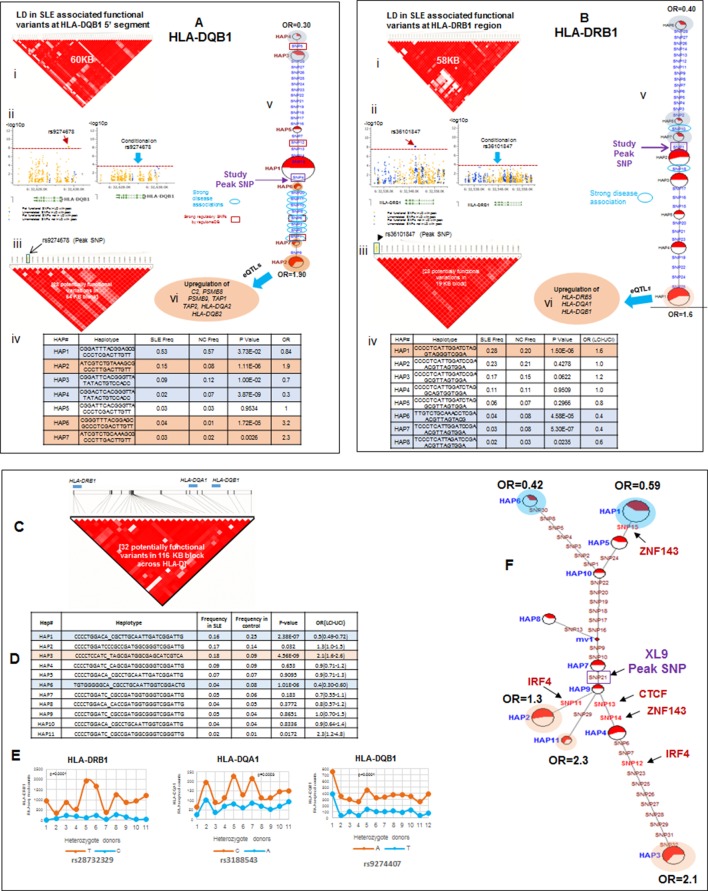
Figure 8. LD structure, haplotypes and MJ network analysis in HLA-DQB1 and HLA-DRB1 region.
(A) (i) LD structure at HLA-DQB1 5’ region generated with 68 common (MAF≥10%) potentially functional variants in 1349 samples. (A) (ii) Zoom Manhattan plot showing SLE variant association levels and conditional analysis on peak SNP rs9274678. (A) (iii) LD block structure of 28 potentially functional SLE associated SNPs which are used for downstream haplotype analysis. (A) (iv) Haploview generated seven haplotypes from these 28 functional variants. Frequencies in cases and controls and association statistics are provided. Risk (red) and protective (blue) haplotypes are color highlighted. (A) (v) MJ networks analysis to illustrate divergence of risk and protective regulatory haplotypes. (A) (vi) eQTL variations from public databases for variants in strongest risk haplotype. (B) (i) LD structure at HLA-DRB1 region generated with 66 common (MAF≥10%) potentially functional variants in 1349 samples. (B) (ii) Zoom Manhattan plot showing SLE variant association levels and conditional analysis on peak SNP rs36101847. (B) (iii) LD block structure of 28 potentially functional SLE associated SNPs which are used for downstream haplotype analysis. (B) (iv) Haploview generated eight haplotypes from these 28 functional variants. Frequencies in cases and controls and association statistics are provided. Risk (red) and protective (blue) haplotypes are color highlighted. (B) (v) MJ networks analysis to illustrate divergence of risk and protective regulatory haplotypes. (B) (vi) eQTL variations from public databases for variants in strongest risk haplotype. Panel (C) 116 kb LD block generated with 32 SLE associated potentially functional variations from the three independent association signals in HLA-D region. (D) Haplotype association statistics in cases and controls with risk (red) and protective (blue) haplotypes highlighted. (E) Allelic bias in level of transcription for HLA-class II genes between SLE risk and non-risk alleles in 11 independent heterozygous donors (measured as shown in Figure 6). Number of RNA sequencing reads were compared between chromosome carrying risk (orange line) verses non-risk (blue line) allele for each class II gene. (F) MJ network analysis illustrating the relationships of risk and non-risk haplotypes based on 32 functional variations. SLE associated variants sitting exactly within specific protein binding motifs i.e. IRF4, CTCF and ZNF143 are highlighted with arrows.