Figure 2.
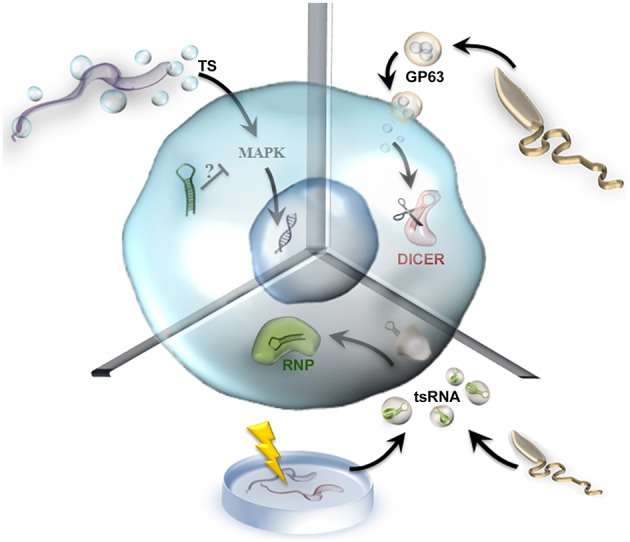
Transfer of parasitic extracellular vesicle cargo to host cells. In this figure, we used a generic host cell to exemplify three different molecules delivered by parasitic extracellular vesicles. In the upper left part of the diagram, Trypanosoma cruzi releases EVs containing TS (trans-sialidase, blue circles) that can trigger gene modulation through the MAPK signaling pathway, which may be regulated by microRNAs. In the upper right part of the diagram, Leishmania donovani releases GP63 vesicles (orange circles) that cleave DICER (red), impairing microRNA maturation. Finally, in the bottom part of the diagram, EVs containing tsRNA (tRNA-derived small RNAs, in green) from Leishmania and from stressed Trypanosoma cruzi parasites modulate gene expression and might form RNP complexes (green).
