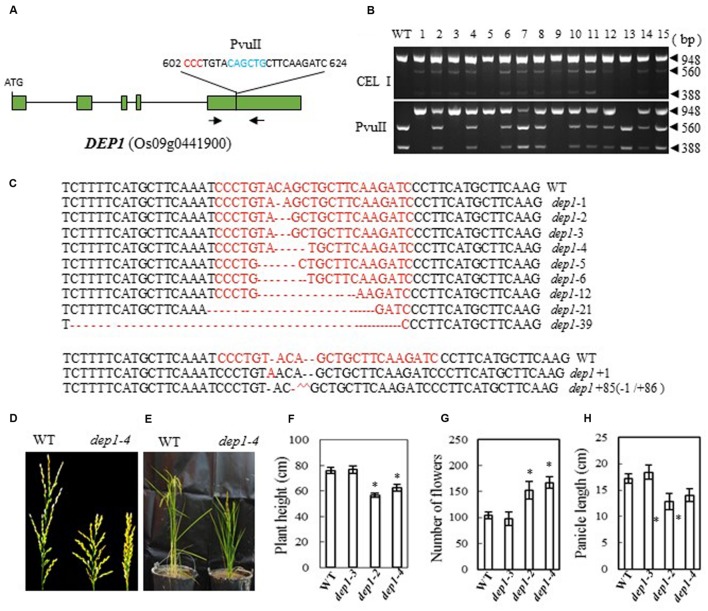
FIGURE 2.
CRISPR/Cas9-induced Dep1 mutant plants and phenotype analysis. (A) Schematic map of the genomic region of DEP1 and the sgRNA target site; arrows show the positions of PCR primers used for mutation detection; The PAM motif (NGG) is shown in red; Restriction site is shown in blue; (B) Gel electrophoresis of PCR products amplified from the mutated region digested with CEL I (upper panel) and PvuII (lower panel); WT and 1–15 are DNA samples from wild type and different transgenic plants. Arrows show the expected band sizes after CEL I or PvuII digestion. (C) Sequence alignment of the sgRNA target region showing altered bases in different mutant lines; (D) Representative pictures showing the morphology of the main panicle; (E) Phenotype of the mutant plants grown in a greenhouse; statistics for plant height (F), number of flowers per main panicle (G) and panicle length (H) of representative mutant plants. Data were collected from 10 to 15 plants per mutant line. * indicates a significant difference (P < 0.05) in comparison to WT controls.