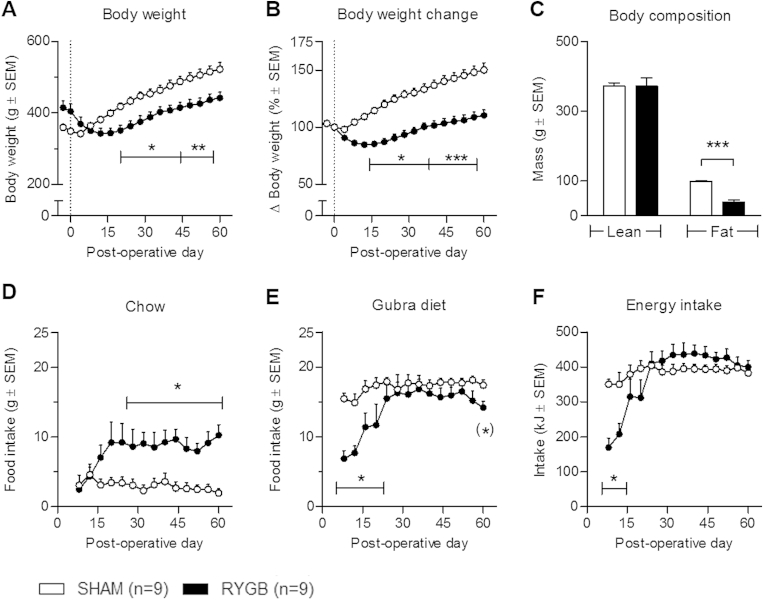
Figure 1.
Body weight and food intake in RYGB and SHAM animals. RYGB surgery led to a sustained decreased in body weight relative to sham (A + B) as well as a significant reduction in body fat mass (C). RYGB induced a persistent significant increase in chow intake (D) whereas Gubra diet intake (E) and total energy intake (F) were similar between sham and RYGB after an initial recovery period. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. On the day of euthanization (day 60) the intake of Gubra diet was significantly reduced in the RYGB group (E); student's unpaired t-test (*)p < 0.05.