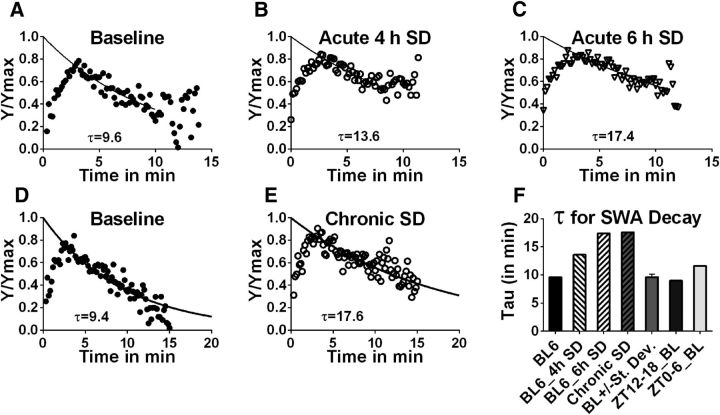
Figure 1.
SWA decay time constant correlates with sleep need in wild-type mice. The time constant of SWA decay (τ) during an average SWS episode following differing amounts of SD is determined by a single phase exponential, regression fit in wild-type mice. The conditions for C57BL/6 mice include baseline, 4 and 6 h acute SD (A–C, respectively). D, E, The pooled group of genetic control strains (BL6_Tam, fAdK_Tam, fAdK;GFAP:CreER_Veh) experienced chronic SD (4 h SD with 2 h recovery for 8 consecutive cycles). Plots represent time of the SWS episode (plotted for each 10 s epoch; x-axis) versus normalized SWA (y-axis). F, Histogram of SWA decay during an average SWS episode determined for each SD condition shows a graded slowing in proportion to previous enforced W duration. “BL+/−St. Dev.” is a pooled control strain used for chronic SD. The τ determined under baseline conditions during either the phase of minimal sleep need (6 h, early part of the active phase, ZT12–18_BL) compared with the phase of high sleep need (6 h, early part of the inactive period, ZT0–6_BL) shows a similar increase in duration with sleep need.