Figure 4.
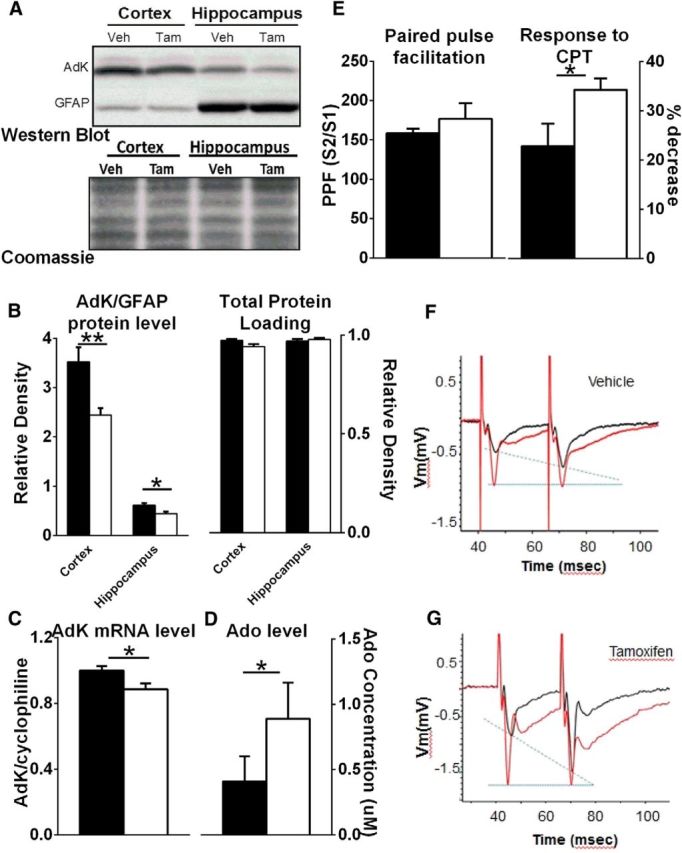
Characterization of AdK knockdown. A, Top, Representative examples of Western blots using AdK (top row) and GFAP (bottom row) antibodies from cortical and hippocampal tissue in one Veh- and one Tam-treated fAdK;GFAP:CreER mouse. Negative images and resized plots are shown. Light upper band represents a nonspecific cross reactive band that is typical for antibodies that detect protein in the 50 kDa range. Dark lower band represents both the short and long AdK isoforms that do not easily resolve (43.5 and 45 kDa, respectively). Bottom, Coomassie stain of total protein from the membrane used for the Western blots shown in top blot. This shows equivalent relative densities of Coomassie stain between genotypes and between regions and demonstrates the loading of equal amounts of protein. Thus, the similarity in GFAP expression between genotypes within the same region and the difference in GFAP expression over different regions is not attributable to differential protein loading (top and bottom blots). B, Tamoxifen decreases AdK protein as measured by quantitative immunoblotting using a monoclonal antibody against AdK (open symbols indicate Tam; closed symbols indicate Veh). AdK level is presented relative to glia-specific GFAP level because AdK is primarily expressed in glia in adults. C, Tamoxifen treatment decreases AdK mRNA as measured by quantitative PCR of fAdK;GFAP:CreER mice (open bars indicate Tam; closed bars indicate Veh). AdK values are presented relative to cyclophilin. D, Knockdown of AdK increases extracellular Ado concentration. Biosensors sensitive to the presence of Ado were used to measure Ado concentration from acute hippocampal slices taken from Veh-treated (filled bar) and Tam-treated (open bar) fAdK;GFAP:CreER animals. Tam-treated mice showed significantly higher Ado levels. E, Paired pulse facilitation, evoked by stimulation of the Schaffer collaterals and recorded as fEPSPs in the stratum radiatum of CA1, was measured in acute hippocampal slices from Veh-treated (filled bar) or Tam-treated (open bar) fAdK;GFAP:CreER animals. The ratios of the evoked response (measured by the slope of the fEPSP) of the second stimulus (S2) to the first stimulus (S1) were compared under baseline conditions (E, left axis; F, G, black traces). PPF indicating presynaptic inhibition is increased in slices obtained from Tam-treated mice. CPT, an AdoRA1 antagonist, blocks PPF (1 μm; F, G, gray traces). The Tam-treated group showed a greater sensitivity of the PPF to CPT, indicating a greater AdoRA1-mediated, tonic, presynaptic inhibition (E, right axis).
