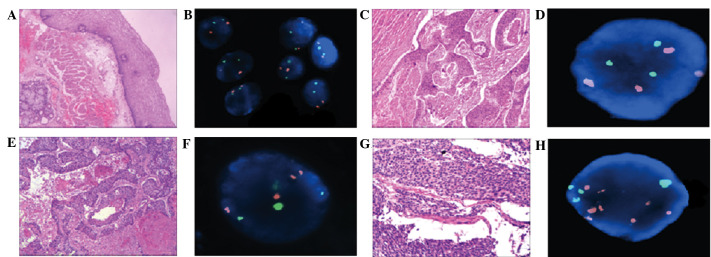
Figure 1.
Comparison of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in normal and abnormal esophageal tissues. (A) Normal esophageal membranes following H&E staining (magnification, 40). (B) Normal representative nuclei carrying 2 copies of the centromeres of chromosomes (CEP) 3 (orange) and 17 (green). (C) Well-differentiated esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) following H&E staining (magnification, 40). (D) FISH representative nuclei carrying 3 copies of CEP 3 and 3 copies of CEP 17. (E) Moderately differentiated ESCC following H&E staining (magnification, 40). (F) FISH representative nuclei carrying 4 copies of CEP 3 and 3 copies of CEP 17. (G) Poorly differentiated ESCC H&E staining (magnification, 100). (H) FISH representative nuclei carrying 7 copies of CEP 3 and 4 copies of CEP 17.