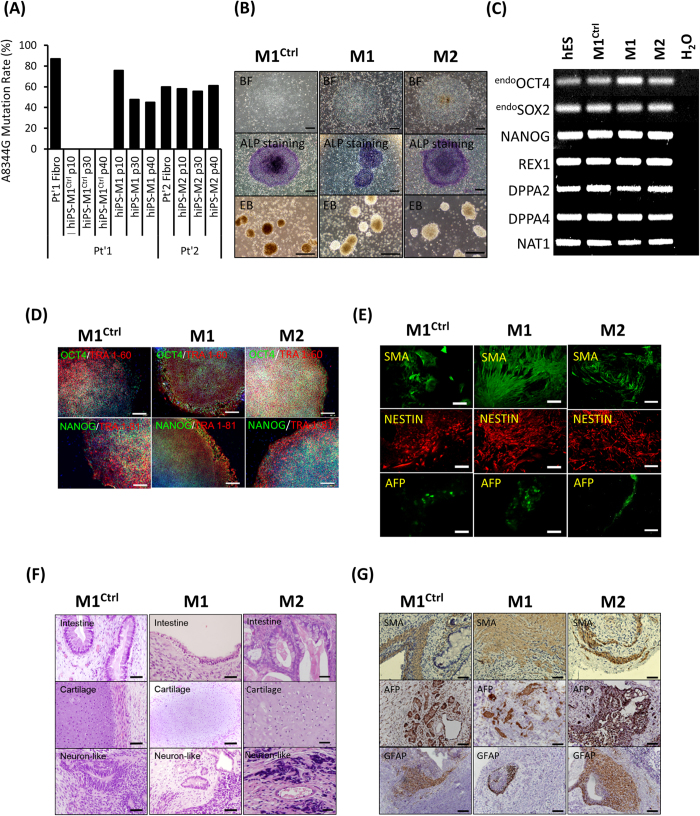
Figure 1. Generation and characterization of hiPSCs harboring mtDNA A8344G.
(A) The mtDNA 8344 alanine to guanine mutation rate was quantified by pyrosequencing fibroblasts from patients with MERRF syndrome and MERRF fibroblast-derived hiPSCs after indicated passages (p10–40). (B) Morphology, alkaline phosphatase activity and embryoid body formation of hiPSCs. Scale bar = 50 μm. (C) Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis indicating the expression pattern of embryonic stem cell-like genes in hiPSC sublines. Human embryonic stem cells (hESC) served as a positive control. H2O served as a negative control. (D) Immunofluorescence analysis revealing the protein expression of pluripotency markers (OCT4, NANOG, TRA 1–81 and TRA 1–60) in hiPSC sublines. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342. Scale bar = 200 μm. (E) In vitro three-layer differentiation of hiPSCs in specific culture medium showing subpopulations of cells that were immunoreactive for SMA (mesoderm), NESTIN (ectoderm) and AFP (endoderm). Scale bar = 100 μm. (F) Sections of teratomas derived from hiPSC sublines showing the differentiation of histologically distinct tissues, including intestine-, cartilage- and neuron-like tissue. Scale bar = 50 μm. (G) Immunohistochemistry analysis of sections of teratomas derived from hiPSC subline using SMA (mesoderm), AFP (endoderm) and GFAP (ectoderm). Scale bar = 50 μm.