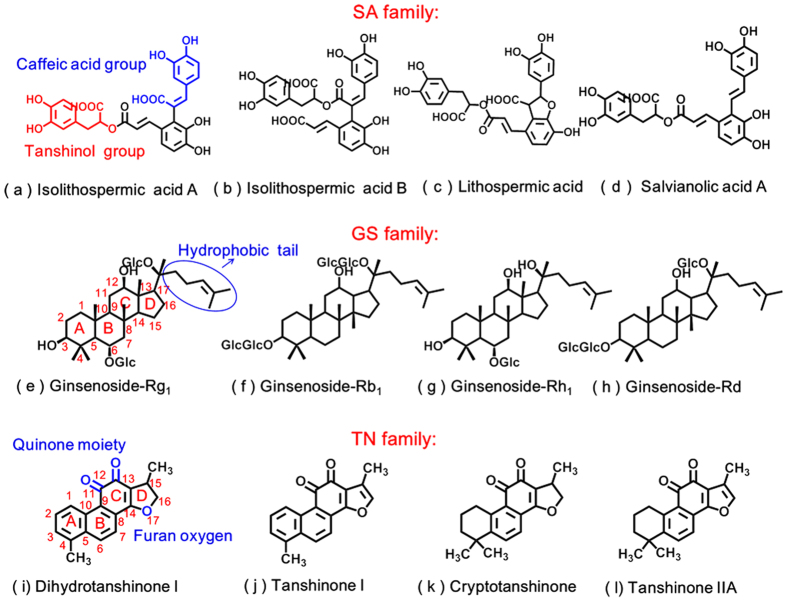
Figure 2. Representative compounds and structural characteristics of SA, GS and TN families in DQP.
SA family includes (a) isolithospermic acid A, (b) isolithospermic acid B, (c) lithospermic acid and (d) salvianolic acid A; SAs are polymers of caffeic acid (C9H8O4) and tanshinol (C9H10O5), of which carboxyl and phenol hydroxyl are two characteristic groups. GS family includes (a) ginsenoside-Rg1, (b) ginsenoside-Rb1, (c) ginsenoside-Rh1 and (d) ginsenoside-Rd; GS has a nucleus with 17 carbon atoms arranged in four rings, to which the hydrophobic tail structure and hydrophilic sugar moieties are attached. TN family includes (a) dihydrotanshinone I, (b) tanshinone I, (c) cryptotanshinone and (d) tanshinone IIA; TN also possesses a similar 17-atom skeleton, but the quinone moiety in the C-ring, furan oxygen in the D-ring and numerous conjugated double bonds make it different.