Fig. 5.
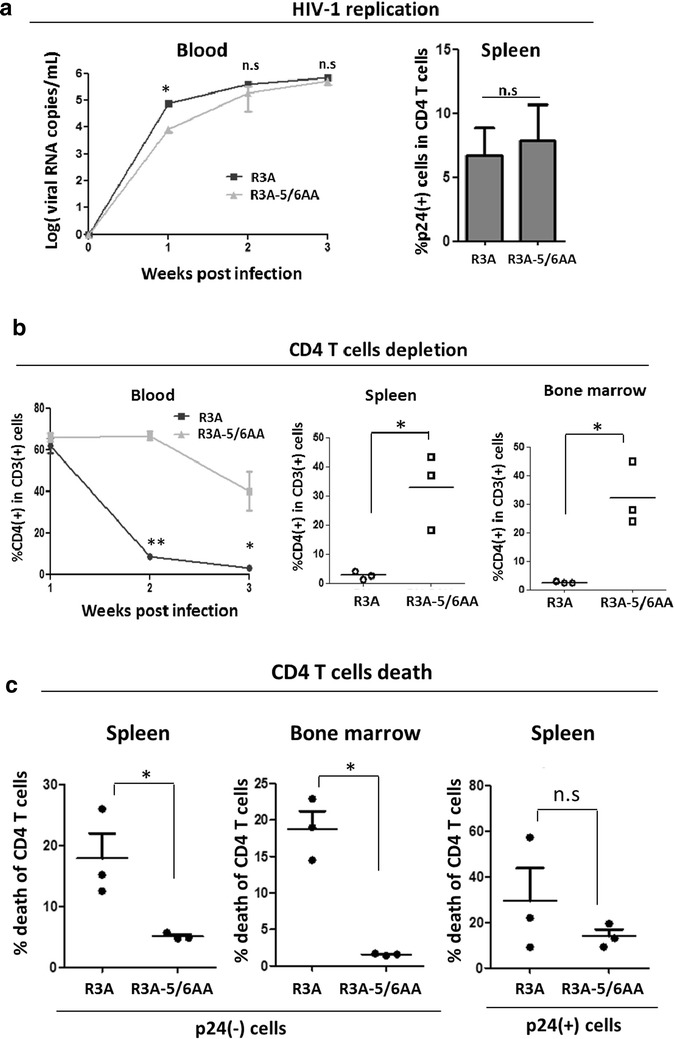
Ablation of CCR5 usage reduces pathogenesis of dual tropic HIV-1 in a humanized mouse model. a Humanized mice were infected with R3A or R3A-5/6AA as described in “Methods” section. Viral replication was assessed weekly by RT-qPCR measurement of HIV-1 genomic RNA in the blood. HIV-1 infection in CD4 T cells was analyzed by intracellular p24 staining of splenocytes isolated from infected mice at 3 weeks post infection (wpi). b Total PBMCs in blood, spleen and bone marrow from infected animals were harvested at 3wpi, and CD4 T cell depletion was analyzed by FACS staining as described in Fig. 1b. c p24(−) and p24(+) CD4 T cell viability in R3A versus R3A-5/6AA infection in the infected animal’s spleen and bone marrow were analyzed as described in Fig. 1c. *p < 0.05
