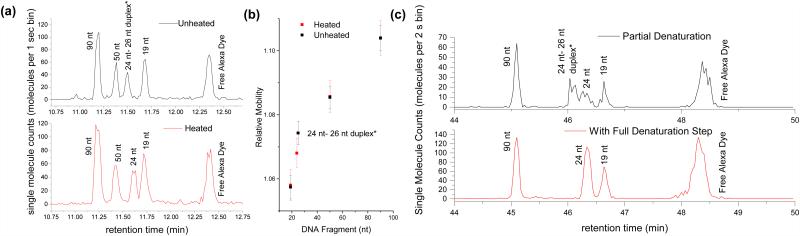
Figure 5.
Denaturation of a double stranded DNA duplex into single strands results in a relative mobility shift. (a) A sample consisting of three single stranded species (19 nt, 50 nt, and 90 nt) and one double stranded species (24 nt – 26 nt duplex*) is separated in a 1.6 μm capillary at room temperature (top) and after heating the sample to 95 C for 5-10 min (bottom). (b) The average relative mobilities from the chromatograms in (a) is plotted against species size to illustrate that only the duplex mobility is affected by heating. (c) High pH environments (top – 1 mM NaOH; bottom 10 mM NaOH) also exhibit denaturation-induced mobility shifts for the duplex species only. Error bars represent the width of each fragment’s elution peak, which was calculated as 4 times the standard deviation of the fitted Gaussian peak.