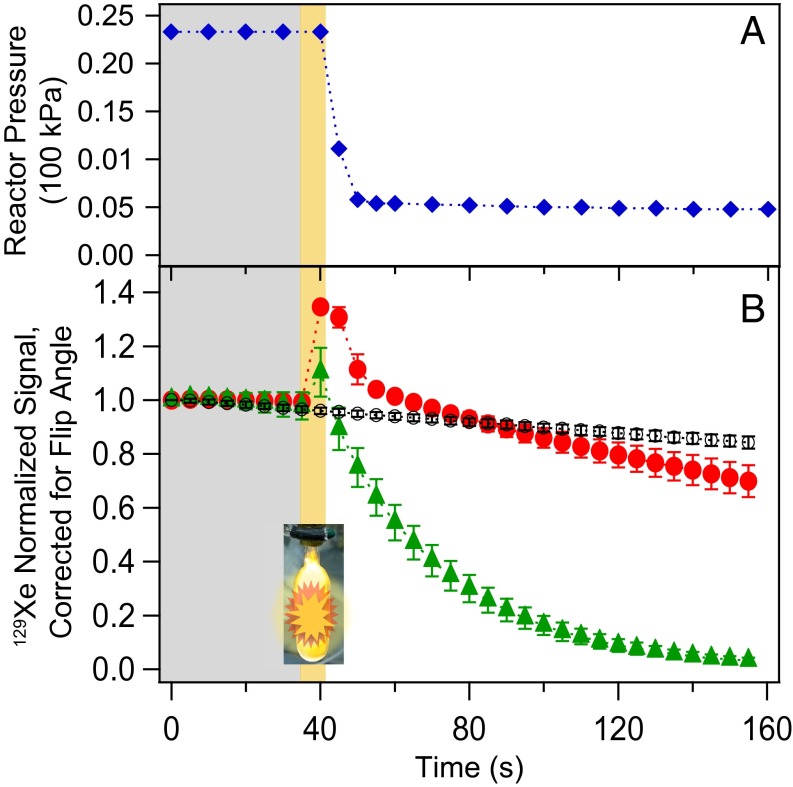
Fig. 3.
(A) In situ reactor pressure measurements (blue diamonds) during the combustion reaction of a 5% Xe/95% H2 gas mixture, with oxygen reservoir tap (tap C, Fig. 2A) opened at t = 40 s adding 11.2 ± 0.4 kPa partial pressure of O2. Average initial partial pressure of H2 = 22.0 ± 1 kPa and the oxygen addition caused the pressure drop due to the combustion reaction (a short term pressure increase, if present, was not observed at the time resolution of the gauge). (B) NMR measurements performed in separate experiments without pressure gauge (i.e., tap B, Fig. 2A was kept shut to reduce the dead volume of the experiment). Normalized integrated hp 129Xe NMR signals following a 9° pulse during the catalytic oxidation with 13.4 ± 0.4 kPa oxygen (red circles) or 20.5 ± 0.5 kPa (green triangles) added at t = 40 s. Average initial partial pressure of H2 = 25.5 ± 1 kPa. Control signals with no oxygen/combustion (tap C, Fig. 2A, remained closed) shown as black open circles. Signal intensity data were corrected for flip-angle attenuation and are the average from three repeat measurements.