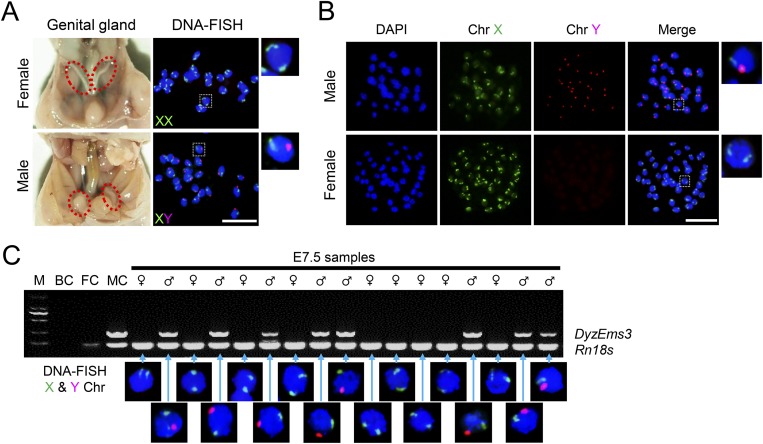
Fig. S1.
Methods for sex determination. (A) At E19, the sex of fetuses was determined based on anatomical observation of the genital glands. To validate the results, 20 randomly selected fetuses were examined using DNA-FISH against the X and Y chromosomes; these results agreed with the anatomical analyses. (B) At blastocyst stage, the sex of blastocysts was determined using DNA-FISH. (Rightmost panels) Higher magnification of boxed regions. (C) At E7.5, epiblasts were isolated from embryos by microdissection, and the sex was determined by PCR. In female samples, only one amplicon corresponding to the Rn18S gene was detected. In male samples, an additional amplicon corresponding to the Y chromosome-specific DyzEms3 segment was detected. Template DNA samples from adult male and female somatic cells were used as the male control (MC) and the female control (FC), respectively. A blank control (BC) without template (water blank) was also examined. To exclude possible cross-contamination between samples, 17 randomly selected embryos were further validated using DNA-FISH. Results are positioned relative to the corresponding PCR sample. M, marker. (Scale bar, 50 μm.)