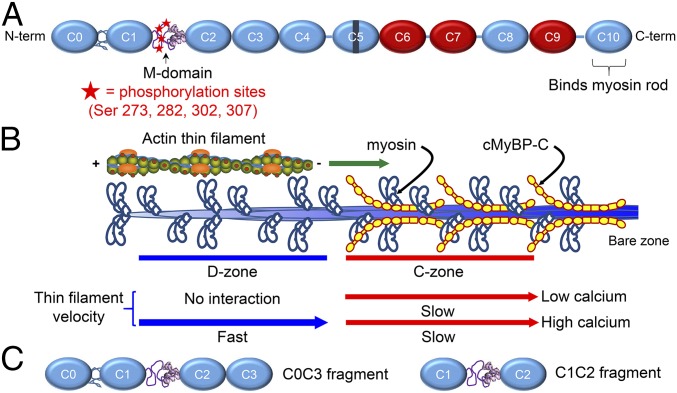
Fig. 1.
Structure and function of cMyBP-C. (A) Schematic diagram of full-length cMyBP-C. Domains C1 and C2 are connected by the M-domain, containing an intrinsically disordered N-terminal region with four phosphorylatable serines, and a more structured C-terminal half. Ig-like domains are shown in blue, and Fn-like domains are shown in red. (B) Illustration of half of a native thick filament with a native thin filament landing on the tip of the thick filament and being translocated through the D- and C-zones at the different speeds indicated, as observed in the TIRFM experiments. (C) Wild-type C0C3 and C1C2 N-terminal fragments used in motility, AFM, and EM assays. Phosphomimetic counterparts to each fragment were expressed containing aspartic acid substitutions for the four serines highlighted in A.