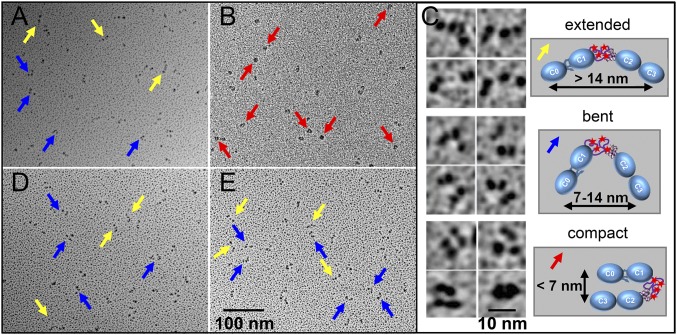
Fig. 5.
Effects of phosphorylation and calcium on the orientation of the N-terminal domains. (A and B) Rotary-shadowed EM images of nonphosphorylated wild-type C0C3 (A) and phosphomimetic C0C34D (B) fragments in the absence of calcium. (C) Representative EM images (Left) and schematic diagrams (Right) of the extended rods (Top), bent rods (Middle), and compact/closed structures (Bottom) classified in each EM image. (D and E) Rotary-shadowed EM images as in A and B for C0C3 (D) and C0C34D (E) fragments in the presence of calcium. Yellow, blue, and red arrows point to molecules with extended, bent, and compact structures, respectively.