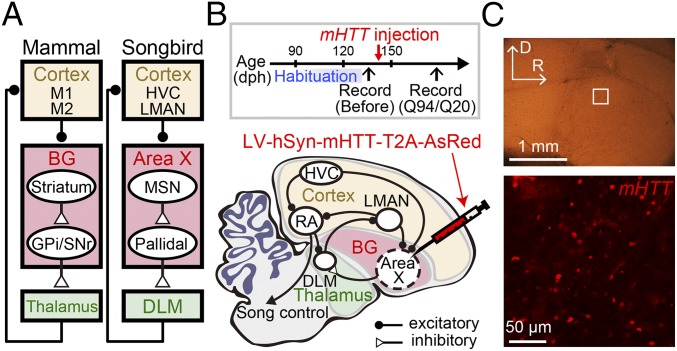
Fig. 1.
Expression of mHTT in the songbird BG. (A) Simplified schematic showing some of the common features of mammalian and songbird cortico-BG networks. (B) Time line of experiments (Top) and a schematic showing a part of the neural circuitry involved in singing behaviors in the songbird (Bottom; sagittal view with rostral to the right and dorsal upward). LV containing a mutant form of mHTT and a fluorescent reporter, AsRed, with insertion of a self-cleaving T2A sequence was injected into the songbird BG (area X) of adult male zebra finches. The songs before injection (habituation) were highly stable (Fig. S1). Behavioral or neural changes were assessed at >30 d after injection. dph, days posthatch. (C) Square region in area X in a sagittal brain slice (Top; D, dorsal; R, rostral) was imaged 34 d after injection with a confocal microscope (Bottom) to confirm expression of mHTT-Q94, as revealed by coexpressed AsRed (see also Fig. S1).