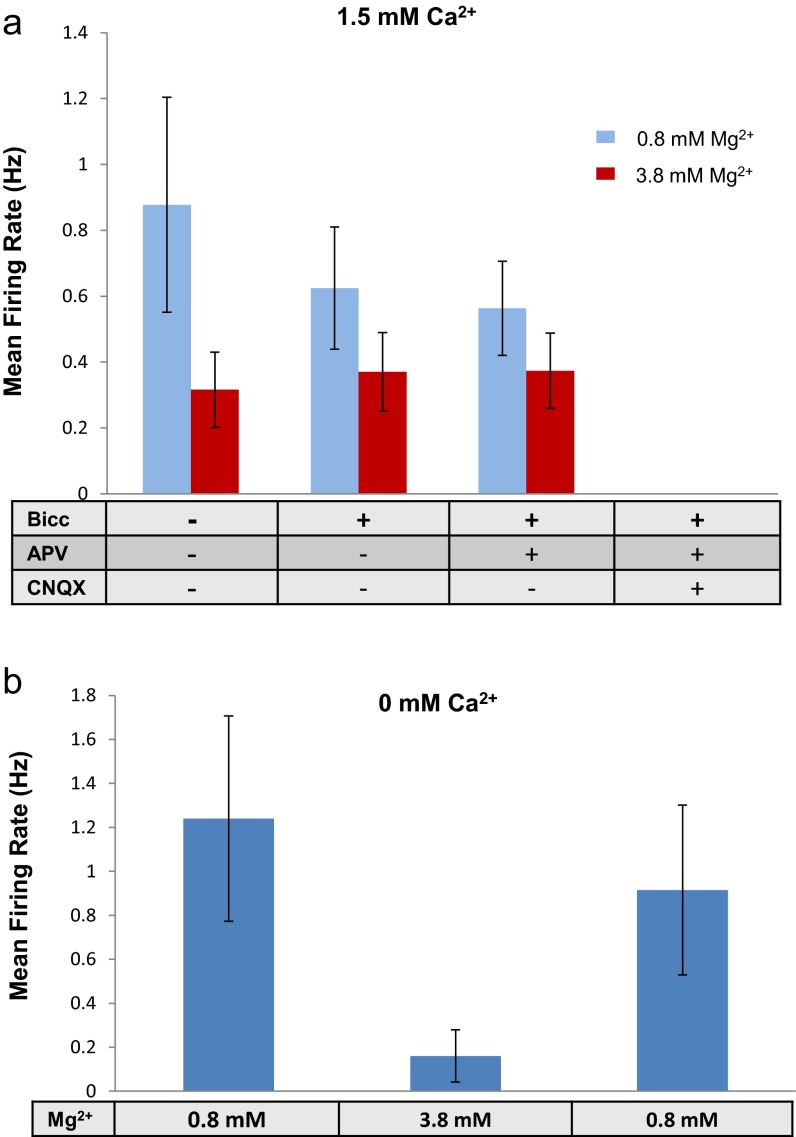
Fig. S7.
Synapse-independent effect of elevated extracellular Mg2+ on single neuron firing rate. (A) Divalent ion magnesium (3 mM) was added to a medium containing the physiological magnesium concentration (0.8 mM) in the presence of 1.5 mM Ca2+. A high magnesium concentration considerably reduced the firing rate. Synaptic blockers were then added to control for a specific magnesium effect stemming from increased blockage of NMDA receptors. Indeed, addition of GABA and NMDA blockers in the presence of high magnesium had no further effect on the mean firing rate of single neurons. As shown in Fig. 1, complete synaptic blockage in the presence of 1.5 mM Ca2+ eliminated all activity. (B) Similar effect of magnesium was also found at a 0 mM extracellular concentration of Ca2+.