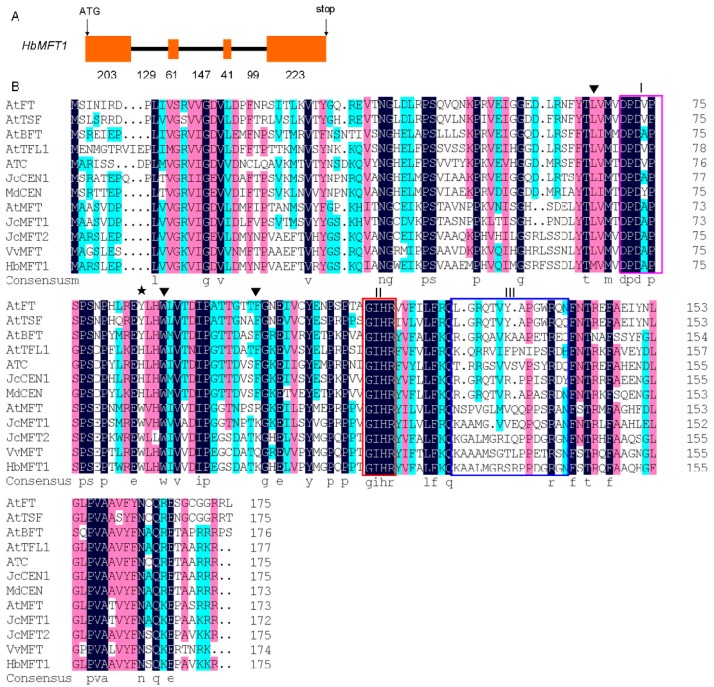
Figure 1.
(A) Genomic organization of HbMFT1. Yellow boxes represent exons. Lines represent introns; (B) Protein multiple alignment between deduced amino acid sequence of HbMFT1 in rubber tree and phosphatidyl ethanolamine-binding protein (PEBP) family of other species. Sequence alignment was carried out using DNAMAN 6.0 software (http://www.lynnon.com/). Three triangles refer to the intron positions. I, D-P-D-x-P motif. II, G-x-H-R motif. III, the region is essential for FT/TFL1-like activity in exon IV. An asterisk indicates amino acids that are related to antagonistic functions between TFL1 and FT protein. Different colors refer to the different homology levels of aligned amino acid residues among MFT homologs. Darkblue represents 100% identity. Hotpink represents more than 75% identity. Turquoise represents more than 50% identity. The aforementioned proteins and their accession numbers: Arabidopsis (AtMFT, NP_173250.1; AtFT, NP_176726.1; AtTSF, NP_193770.1; AtBFT, NP_201010.1; AtTFL1, NP_196004.1; ATC, NP_180324.1), Jatropha curcas (JcCEN, NP_001295672.1; JcMFT1, KC874668; JcMFT2, KF944352), Malus domestica (MdCEN, NP_001280770.1), Vitis vinifera (VvMFT, NP_001267935.1).