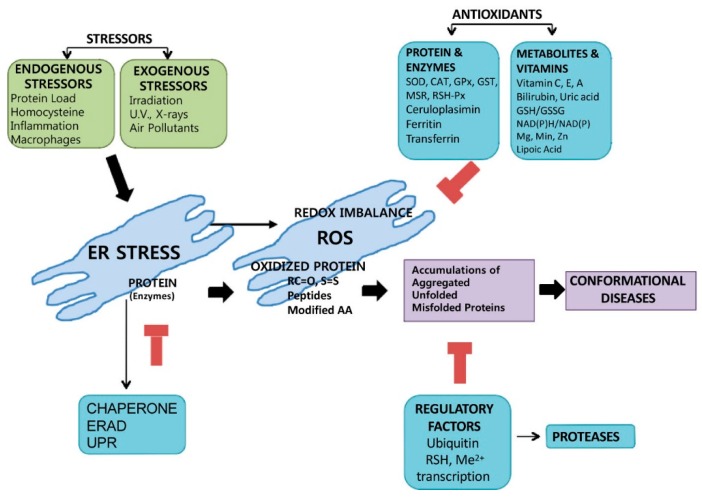
Figure 2.
Aggregation of oxidized proteins depends on the balance of redox signaling mediators, anti-oxidants, pro oxidants, and proteolytic activities in the ER. In the presence of stressors, redox imbalance causes a protein load that leads to ER stress. Then, accumulation of oxidized proteins causes the aggregation, misfolding, or unfolding of proteins and thus the occurrence of conformational diseases. SOD, superoxide dismutase; CAT, catalase; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GST, glutathione transferase; MSR, methionine sulfoxide reductase; RSH-Px, thiole specific peroxidase. The black arrows are showing the stimulation or the flow of mechanism, while red/T-like arrows are showing the blocking of the process.