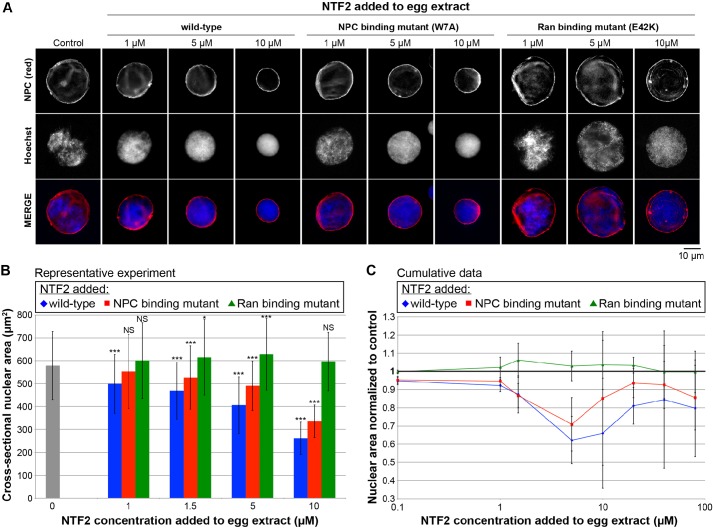
Fig. 1.
Binding of Ran to NTF2 is required for NTF2 to affect nuclear size in X. laevis egg extract. (A) X. laevis egg extract was supplemented with recombinant wild-type and mutant NTF2 proteins at the indicated final concentrations, and the same total volume was added to each reaction. For the control reaction, an equal volume of NTF2 storage buffer was added. Nuclei were assembled and growth was allowed to proceed for 90 min at 20°C. Given that nuclei expand continuously in egg extract, this time point serves as a proxy for the nuclear expansion rate, and at this time nuclei have nearly reached their largest size before physical integrity of the nuclear envelope becomes compromised (Levy and Heald, 2010). Nuclei were fixed, spun onto coverslips, processed for immunofluorescence and stained with mAb414 to visualize the NPC (red) and Hoechst 33342 to visualize the DNA (blue). Representative images are shown. The NPC-binding mutant is NTF2 W7A, and the Ran-binding mutant is NTF2 E42K. (B) Nuclear size data are shown from one representative experiment as described in A. For each bar, the cross-sectional areas of 125–643 nuclei were measured from NPC-stained nuclei and averaged. The error bars are s.d. *P<0.05; ***P<0.001; NS, not significant (compared with the buffer addition control; two-tailed Student's t-test). (C) Cumulative data from 32 different X. laevis egg extracts treated as described in A. The average cross-sectional nuclear areas were measured as in B and normalized to the buffer addition control (bold horizontal line set at 1.0), due to variability between egg extracts. Normalized nuclear areas were averaged across multiple experiments. The error bars are s.d. A subset of experiments was performed in which NTF2 proteins were added to X. laevis egg extract containing nuclei pre-assembled for 35 min followed by an additional 75-min incubation period. Similar nuclear size effects were observed, so these data were averaged along with the data in which NTF2 protein was added to extract at the beginning of nuclear assembly. For the wild-type and NPC-binding mutant, all normalized nuclear area data points are statistically different from the buffer control (1.0) by at least P<0.05; for the Ran-binding mutant, the 10 µM data point is the only one that is statistically different from the buffer control, with P<0.05 (two-tailed Student's t-test).