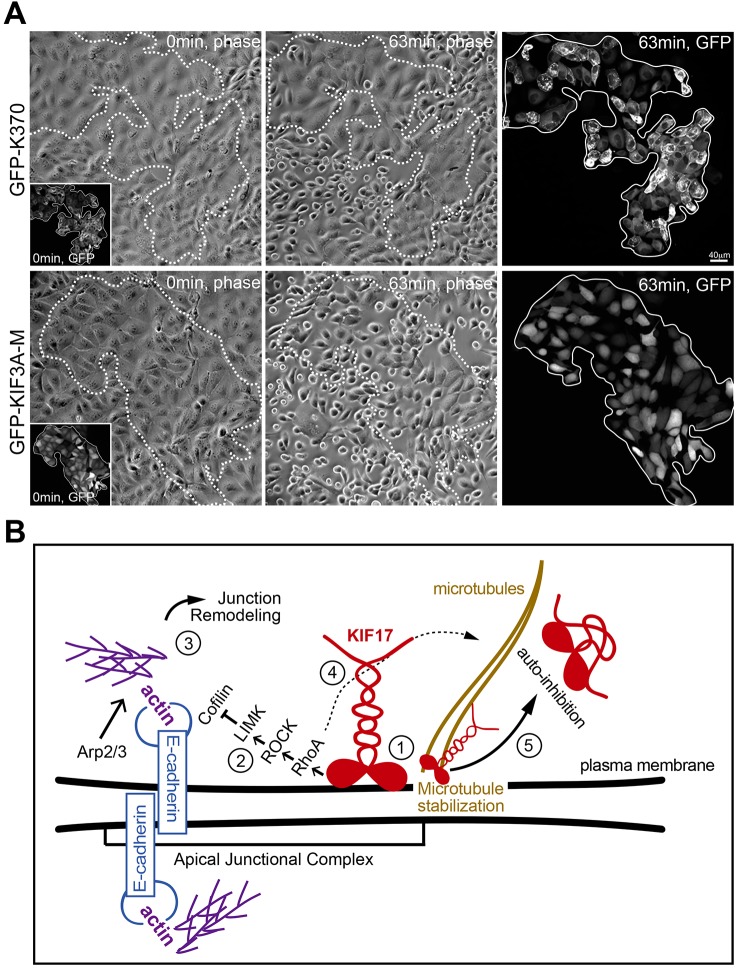
Fig. 8.
K370 strengthens cell–cell adhesions to challenge with calcium chelators. (A) Phase-contrast and fluorescence images showing first and last frames from a time-lapse recording of MDCK cells incubated with 1.5 mM EDTA. EDTA was added 4 h after cDNA injection and cells were imaged at 1-min intervals. Upper panels show cells expressing GFP–K370. Lower panels show cells expressing GFP–KIF3A-M. Insets show GFP fluorescence of expressed constructs at the start of the recordings. Outlined regions on phase-contrast images show the area encompassed by GFP–KIF-expressing cells. Fluorescent images on the far right show GFP–KIFs at the last frame of the time-lapse. (B) Model for KIF17 function at the AJC of epithelial cells: (1) KIF17 associates with the AJC, where it colocalizes with E-cadherin and junctional actin. (2) The KIF17 motor domain is sufficient for junctional localization and triggers activation of a RhoA signaling pathway leading to inhibition of cofilin. (3) Decreased cofilin severing activity allows for the accumulation of junctional actin, alters E-cadherin trafficking and impairs junction dissociation in response to calcium depletion. (4) KIF17 also regulates microtubule stabilization (Jaulin and Kreitzer, 2010), likely downstream of RhoA signaling. (5) KIF17 functions at the AJC and on microtubules are inhibited by intramolecular interactions between the motor and tail domains.