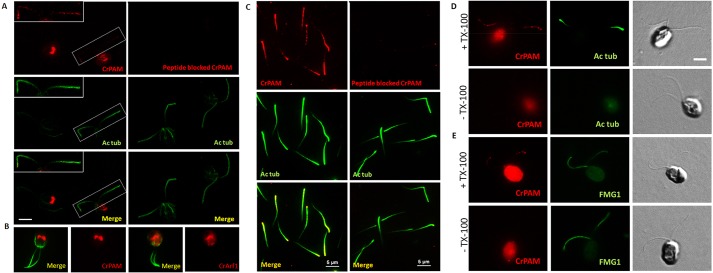
Fig. 5.
CrPAM localizes to the Golgi and cilia in cell-wall-deficient CC4351 Chlamydomonas cells. (A) Confocal images of Chlamydomonas cells fixed, permeabilized and immunostained with affinity-purified antibody to CrPAM and acetylated tubulin (Ac tub, left) and the corresponding peptide-blocked control (right). CrPAM displayed tubulovesicular localization at the center of the cell body and punctate staining along the length of the cilia (white box and inset). Scale bar: 5 µm. The CrPAM signal was eliminated when antibody was pre-incubated with antigenic peptide. (B) CrPAM staining in the cell body of fixed and permeabilized cells resembled CrArf1 staining. (C) Cilia isolated from CC124 Chlamydomonas were fixed, permeabilized and immunostained for CrPAM and acetylated tubulin (left); cilia visualized using CrPAM antibody pre-incubated with antigenic peptide served as a specificity control (right). Scale bars: 5 µm. (D,E) Fixed Chlamydomonas were incubated with antibodies to CrPAM and acetylated tubulin (D) or FMG1 (E) in the presence (+TX-100) or absence (−TX-100) of detergent; images for both treatments were acquired under identical conditions. Differential interference contrast images (right panels) allowed identification of cilia. CrPAM and tubulin staining was only observed in TX-100-treated cells. Scale bar: 5 µm.