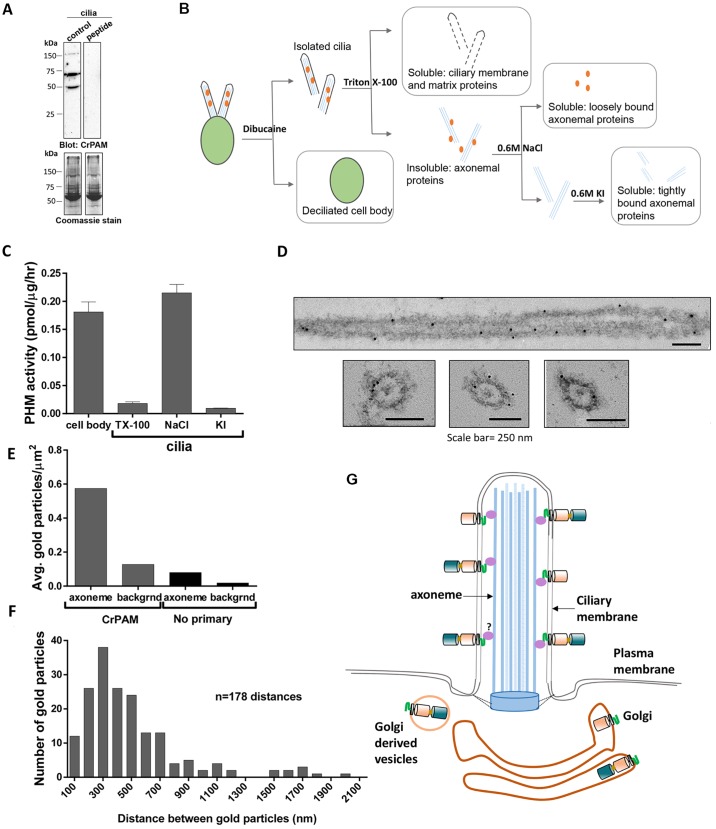
Fig. 6.
CrPAM associates with the axoneme. (A) Isolated Chlamydomonas cilia extracted in SDS-lysis buffer were electrophoresed in a 10% polyacrylamide gel and immunoblotted with antibody against the CrPAM C-terminus (control) and antibody preincubated with a blocking peptide (peptide). Coomassie stain shows equal loading. The C-terminal antibody detected three specific bands. (B) Schematic of fractionation scheme used to enrich for proteins associated with different ciliary sub-structures. Wild-type CC124 Chlamydomonas cilia were sequentially treated with buffers containing 1% Triton X-100 (to solubilize ciliary membrane and matrix proteins), 0.6 M NaCl (to solubilize proteins associated with the axoneme) and 0.6 M KI (to solubilize the axoneme and tightly bound proteins). Deciliated cell bodies were solubilized in 1% Triton X-100. (C) PHM-specific activity in Triton X-100 (TX-100)- and salt-extracted fractions obtained from cilia and cell bodies with the fractionation scheme described in B. Data shown are mean±s.d. (n=2) from one of two experiments, which yielded similar results. (D) Immunoelectron microscopy images of CrPAM localization in detached cilia from wild-type CC124 Chlamydomonas. Gold particles were observed on or very close to the axonemal surface in both longitudinal and transverse sections. (E) The average density of gold particles in at least 50 axoneme and background regions was quantified for axonemes stained using the anti-CrPAM antibody and control (no primary antibody). Gold particles separated by more than 20 nm from the axoneme were considered background. The axonemal membrane is not visible because osmication was not performed. (F) To search for periodicity, the distance between adjacent gold particles on the same side of the axoneme was determined. The histogram was created using a 100-nm bin size; n=178 distances. (G) Model of CrPAM localization in C. reinhardtii Golgi and cilia. Multiple forms of CrPAM generated by proteolytic processing are present in the cilium and cell body (only the full-length form and CrPAL membrane-anchored forms are shown). The C-terminal domain resides in the cytoplasm in the cell body and in the ciliary matrix. The tight association of CrPAM with the axoneme could be indirectly mediated by unknown protein(s) depicted in purple.