Fig. 2.
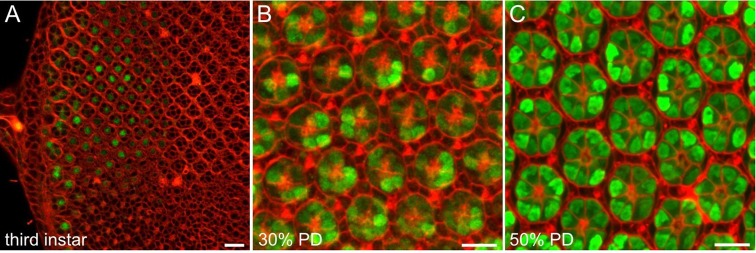
In vivo imaging shows Ire1 activity early in R cell differentiation. (A) In a live third-instar eye disc, FM4-64 (red) marks cell outlines, whereas MXG reports Ire1 endonuclease through GFP (green) expression in R8 cells at the posterior of the disc. R cell nuclei occupy stereotyped planes in the developing third-instar eye (Tomlinson, 1985) and the R8 nuclear plane at the posterior of the disc is highlighted by GFP. Anterior is to the right and the morphogenetic furrow is close outside the frame. (B) In a confocal z-stack composite of a live 30% pupal development eye, FM4-64 (red) shows the immature, unresolved apical tiling of interommatidial cells in a single optical section overlaid on a maximum intensity projection of optical sections of underlying R cell nuclei; GFP (green) shows Ire1 activity in many R cells. (C) A composite confocal z-stack image of a live 50% pupal development eye. A single optical plane FM4-64 (red) shows the resolved interommatidial cell lattice image and ‘wagon wheel’ R cell organization overlaid on maximum projection through underlying R cells. All R cells express GFP (green). Scale bars: 10 μm.