Fig. 1.
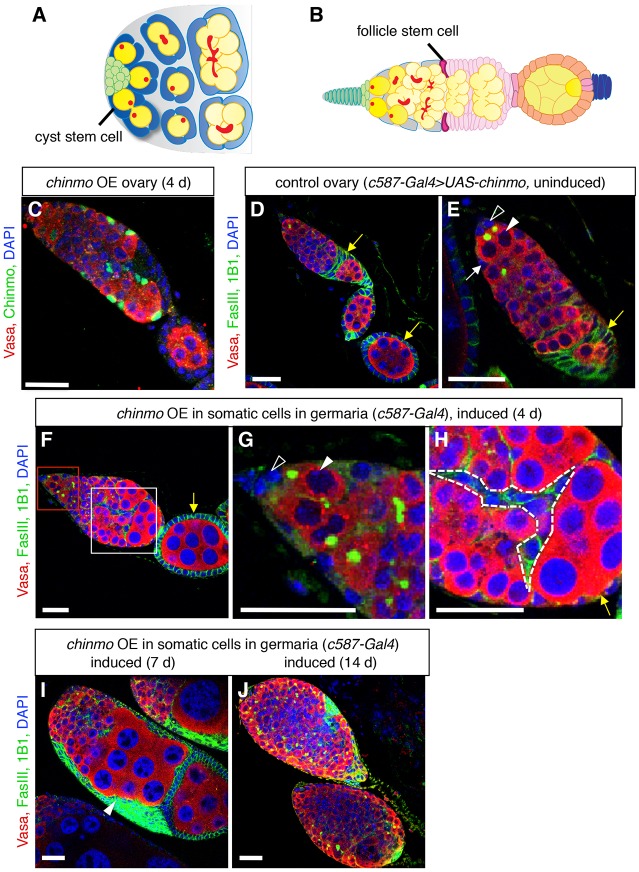
Ectopic expression of chinmo in somatic cells of adult germaria disrupts oogenesis. (A) Illustration of a wild-type Drosophila testis apex (adapted from de Cuevas and Matunis, 2011). Germline stem cells (GSCs, dark yellow) and somatic cyst stem cells (cyst stem cells, dark blue) adhere to the hub (green). GSCs, which contain spherical fusomes (red), produce differentiating male germ cells (spermatogonia, yellow), which contain branched fusomes. Approximately two somatic cyst stem cells flank each GSC; cyst stem cells produce squamous, quiescent cyst cells (light blue), which encase differentiating germ cells. (B) Illustration of a wild-type Drosophila germarium and egg chamber (adapted from Ma et al., 2014). Terminal filament cells (dark green) and cap cells (light green) support GSCs (dark yellow), which produce differentiating female germ cells (light yellow). Escort cells (gray) surround dividing germ cells in the anterior half of the germarium. Two somatic follicle stem cells (follicle stem cells, magenta) produce follicle precursor cells (light pink), which differentiate into follicle cells (orange) and stalk cells (blue). Each egg chamber contains a cluster of 16 germ cells surrounded by a monolayer of columnar epithelial follicle cells. Egg chambers are linked by chains of stalk cells. (C) Immunofluorescence detection of ectopic Chinmo protein (green) in an adult ovary. Chinmo is undetectable in wild-type ovaries (Fig. S1H), but after four days of ectopic chinmo overexpression (OE) in somatic cells in the adult germarium, Chinmo is easily detected in the chinmo-expressing cells. (D-J) Immunofluorescence detection in adult ovaries of FasIII (green at cell periphery) to visualize somatic cell membranes, and 1B1 (green in germ cells) to mark fusomes. Before ectopic chinmo expression, the adult ovariole (D) and germarium (E) look normal. GSCs (arrowheads in E,G) are attached to caps cells (open arrowheads in E,G). Escort cells (white arrow) associate with germ cells in the anterior portion of the germarium; follicle cells (yellow arrows), which express higher levels of FasIII, form a monolayer of columnar epithelial cells around germ cells at the posterior end of the germarium. After ectopic chinmo expression in adult somatic cells for four days (F-H), defects in egg chamber formation are apparent. The stem cell niche looks normal (F, magnified in G), but clusters of differentiating germ cells accumulate at the posterior end of the germarium (F, magnified in H). Somatic cells are evident between germ cells (dashed lines in H) and no longer form a regular columnar epithelial monolayer (yellow arrow in H). After ectopic chinmo expression for longer times (I-J), ovaries fail to form normal egg chambers, and germaria are filled with overproliferating early germ cells and somatic cells. In all panels, Vasa marks germ cells (red), DAPI marks nuclei (blue), and anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 20 μm.