Figure 4.
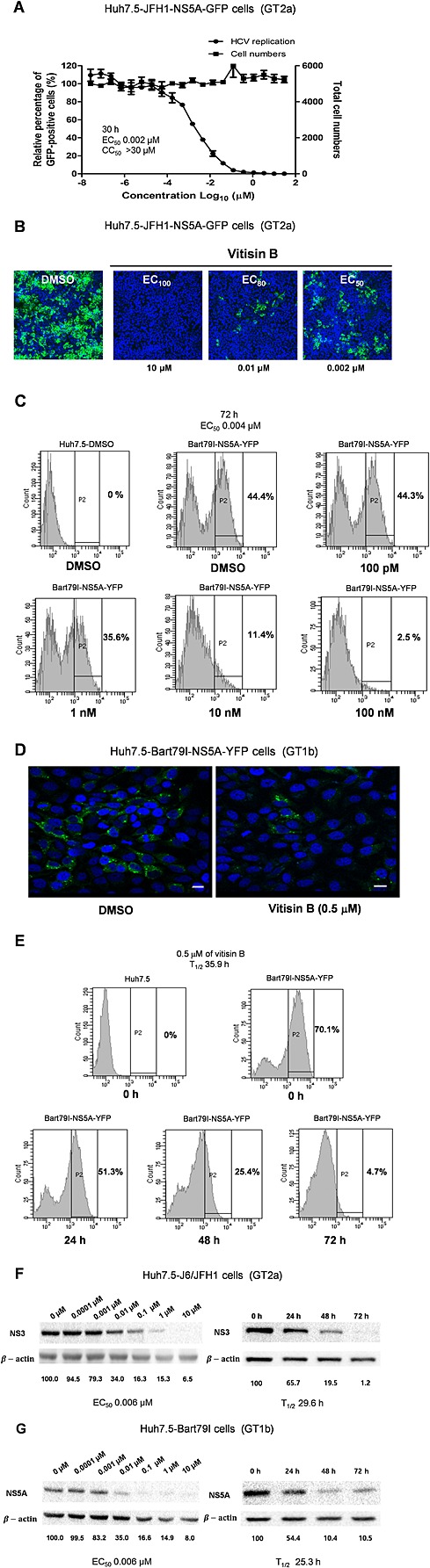
Vitisin B diminishes the expression of HCV proteins. A The dose‐dependent effect of vitisin B on the levels of NS5A protein was determined using HCVcc JFH‐1 cells expressing an NS5A‐GFP fusion protein. The abundance of NS5A protein was assessed by determining the number of NS5A‐GFP‐positive cells, and the total cell number was used as a marker for cytotoxicity. Experiments were performed in duplicate. B Huh‐7.5 cells were pretreated with either DMSO or 10, 0.01 and 0.002 μM vitisin B followed by inoculation with HCVcc for 30 h. The effect of vitisin B on the expression NS5A was determined by visualizing the relative level of NS5A‐GFP via confocal microscopy. Nuclei were stained in blue with DAPI. The images were obtained using a Nikon confocal laser scanning microscope. C The dose‐dependent effect of vitisin B on the levels of NS5A protein was determined by measuring the relative percentages of NS5A‐YFP‐positive cells via FACS analysis of Huh7.5‐Bart79I‐NS5A‐YFP cells treated with increasing concentrations of vitisin B for 72 h. D The effect of vitisin B on the subcellular localization of NS5A protein was determined by visualizing the relative levels of NS5A‐GFP via confocal microscopic analysis of Huh7.5‐Bart79I‐NS5A‐YFP cells treated with either 1% DMSO or 0.5 μM vitisin B for 30 h. Nuclei were stained in blue with DAPI. The images were obtained using a Nikon confocal laser scanning microscope. The scale bar represents 15 µm. E The time‐dependent effect of vitisin B on the levels of NS5A protein was determined by measuring the relative levels of HCV NS5A‐YFP‐positive cells via FACS analysis of Huh7.5‐Bart79I‐NS5A‐YFP cells treated with 0.5 μM vitisin B for increasing periods of time. EC50 and T1/2 values were determined based on each response curve. F and G Dose‐independent and time‐dependent effects of vitisin B on the levels of viral proteins, as well as β‐action proteins, were determined by Western blot analyses of F Huh7.5‐J6/JFH1 or G Huh7.5‐Bart79I cells treated with either increasing concentrations of vitisin B for 72 h or 0.5 μM vitisin B for increasing periods of time.
